https://habr.com/en/post/489624/- Popular science
- Biotechnologies
- Geek health
Translated by authorNovel Coronavirus nCOV/2019-nCoV/NCP/COVID19: Forecasts, Statistics, Protection, News, World: ~2500 [4th reprint, 26.02]
 КДПВ
КДПВ
 In Chinese
hmp.me/cxq9
In Chinese
hmp.me/cxq9

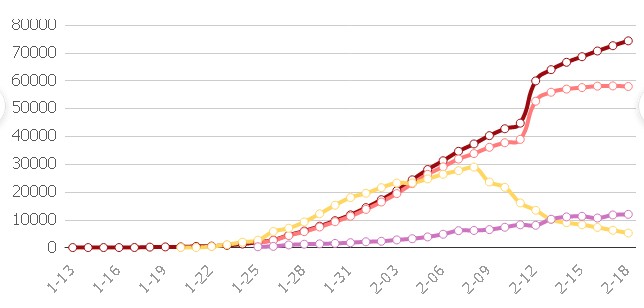
Incomplete data from December 31 to February 19
Incomplete data for the entire period
New news
Updated Charts for 2019-nCov
AbstractAs a result, I managed to indicate in a popular form almost all the features of the coronavirus, talk about the features of protection, predict the probabilities, and indicate the factors influencing the statistics.
I managed to update the information every day for a month. I managed to write about almost everything related to coronavirus.
The publication is too big. 300000 symbols: 13000 (news) + 170,000 (publication). I will not be able to briefly talk about the content.
Follow the links to the topic you need. Do not be afraid about the large article size and complexity. I made the article as clear as possible.
The situation was in an unstable phase and everything could end. But the virus has found new “broad ways” to spread.
Therefore, country information is now important. In the worst case scenario, South Korea will repeat the fate of China.
Russian version
Unfortunately, the quality of the translation may not be ideal. Please indicate errors(Ctrl+Enter).
This is the fourth version of the publication: 200,000 letters + 15,000 news.22.01. You can follow the links where necessary.
The third version(Ru)02/04/100000 letters.
The second version(Ru)28.01.70000 letters.
The first version(Ru)26.01.50000 letters.
Repaired anchors. Links are now clickable:
I fixed the anchors a second time. Now everything is working for sure.
New news
New news:(Changed)
Updated Charts for 2019-nCov
- Extended Facts: Family
- Extended Facts: Typology
- Extended Facts: Size
- Extended Facts: Other
- Extended facts: Structure
- Symptom Data: Invasion
- Symptom Data: Main Symptoms
- Similar signs of three coronaviruses
- Gaps in understanding coronavirus source
- Gaps in understanding:One case from the past ,1
- Gaps in understanding:One case from the past ,2
- Understanding Gaps: Probably Wrong Hypotheses
- Understanding Gaps: A Possible Carrier, Research
- Understanding Gaps: A Probable Virus Carrier, Research,1
- Understanding Gaps: A Probable Virus Carrier, Research,2
- Understanding Gaps: A Probable Virus Carrier, Research,3
- Gaps in understanding the coronavirus Source: A study that was conducted hCoV-EMC
- Gaps in understanding:Summary
- Features of coronavirus, including especially important.
- Features of coronavirus: Incubation period
- Possible origin: Virus transmission methods: Contagiousness (Copy)
- Possible origin: Summary: Action required
- Possible origin:Summary: Suspicion
- Possible origin: Methods of spreading the virus
- Possible origin: Virus transmission methods: Contagiousness (Copy)
- Section 2: A Brief History of Medical Remedies
- Section 2: Features of protection against the virus: Treatment and prevention
- Protection Features: Treatment
- Protection features: Treatment methods. Question from the reader: Effect of ACE2 blockers
- Protection Features: Treatment Methods (Copy)
- Protection Features: Vaccines (Copy)
- Section 2: Features of the virus protection: masks: Pros and Cons
- Why WHO, other doctors do not recommend the use of masks. Why you can still use them
- Cons of PPE
- Pros of PPE
- РSection 2: Features of the virus protection: masks: Features
- Protection Features: Masks: If
- Protection Features: Masks: Disadvantages
- Summary: Respirators can be used.
- Protection Features: Masks: Best Option
- Section 2: Features of virus protection: conventional mask: Research
- Virus survival: The effect of water is mostly positive for the virus. (Copy)
- Summary: Respiratory Filtering Efficiency. (Copy)
- Section 2: Host Coronavirus Adaptability
- Virus Survival: Adaptability of the Virus.
- Virus survival: Interspecific transition.
- Section 2: Introductory information on the survivability of viruses.
- Virus survival: Effect of temperature, a key factor.
- Virus survival: Question from the reader.
- Virus survival: Humidity, an additional factor.
- Virus Survival: Effect of Temperature, Key Factor. (Copy)
- Symptom Data: Invasion
- Symptom Data: Main Symptoms
- Similar signs of three coronaviruses
- Gaps in understanding coronavirus source
- Gaps in understanding:One case from the past ,1
- Gaps in understanding:One case from the past ,2
- Understanding Gaps: Probably Wrong Hypotheses
- Understanding Gaps: A Possible Carrier, Research
- Understanding Gaps: A Probable Virus Carrier, Research,1
- Understanding Gaps: A Probable Virus Carrier, Research,2
- Understanding Gaps: A Probable Virus Carrier, Research,3
- Gaps in understanding the coronavirus Source: A study that was conducted hCoV-EMC
- Gaps in understanding:Summary
- Features of coronavirus, including especially important.
- Features of coronavirus: Incubation period
- Possible origin: Virus transmission methods: Contagiousness (Copy)
- Section 2: A Brief History of Medical Remedies
- Section 2: Features of protection against the virus: Treatment and prevention
- Protection Features: Treatment
- Protection features: Treatment methods. Question from the reader: Effect of ACE2 blockers
- Protection Features: Treatment Methods (Copy)
- Protection Features: Vaccines (Copy)
- Section 2: Features of the virus protection: masks: Pros and Cons
- Why WHO, other doctors do not recommend the use of masks. Why you can still use them
- Cons of PPE
- Pros of PPE
- РSection 2: Features of the virus protection: masks: Features
- Protection Features: Masks: If
- Protection Features: Masks: Disadvantages
- Summary: Respirators can be used.
- Protection Features: Masks: Best Option
- Section 2: Features of virus protection: conventional mask: Research
- Virus survival: The effect of water is mostly positive for the virus. (Copy)
- Summary: Respiratory Filtering Efficiency. (Copy)
- Section 2: Host Coronavirus Adaptability
- Virus Survival: Adaptability of the Virus.
- Virus survival: Interspecific transition.
- Section 2: Introductory information on the survivability of viruses.
- Virus Survival: Effect of Temperature, Key Factor. (Copy)
- Distribution Impact: Summary
- Virus survival: Effect of sunlight activity.
- Virus survival: The effect of water is mainly positive for the virus.
- Summary: Respiratory Filtering Efficiency. (Copy)
- Summary: Why you need to change the mask. (Copy)
- The impact of other measures on the situation
- The impact of other measures on the situation, nose washing, answer to the reader’s question
- Section 2: Factor of virus size, survival and transmission versus all methods
- The effect of other measures on inactivation
- The effect of treatment on inactivation
- The effect of ultraviolet radiation on inactivation, an answer to a reader’s question
- The effect of ozone on inactivation, an answer to a reader’s question
- Section2: Summary: Information about the survivability of the coronavirus on surfaces.
- Probabilities of virus conservation on surfaces: Summary
- Probabilities of virus conservation on surfaces: Summary,2
- Statistics: Learning problems (copy):
- Probabilities of keeping the virus on surfaces without inactivation
- Probabilities of virus conservation on surfaces without inactivation: influence of the main factor
- Section 2: Summary: Virus Potential Viability
- Probabilities of virus conservation on surfaces without inactivation: Summary.
- Summary: Respiratory Filtering Efficiency. (Copy)
- Summary: Why you need to change the mask. (Copy)
- Section 3: Sars Incidence Data (For Comparison)
- SARS Statistics: Cases
- SARS Statistics: Mortality
- SARS Statistics: Mortality by Age
- Section 3: 2019-nCoV incidence data
- Statistics: mortality probability: by age
- Statistics: probability of infection: by age
- Probability statistics for other groups
- Statistics: Cure Probability
- Statistics: death toll (More data in the chart table. From 11.02)
- Statistics: the number of issued
- Statistics: Number of suspicions
- Statistics: number of common cases
- Statistics: number of severe cases
- Statistics: Cumulative cases (More data in the chart table. From 11.02)
- Section 3: Statistics: Country Data
- Section 3: Statistics: Notes and Summary
- Statistics: Results:
- Section 3: Approximate Simple Assessment Scheme
- Statistics: Forecast: Assumptions:
- The characteristics of the coronavirus, including hc, are especially important: Distribution without symptoms (copy)
- The characteristics of the coronavirus, including hc, are especially important: Distribution without symptoms (copy)
- The characteristics of the coronavirus, including hc, are especially important: Distribution without symptoms: Opinion (Copy)
- Summary: Assessment Models for Other Professionals
- Statistics: Forecast: Forecast model, 1
- Statistics: Forecast: Forecast model, 2
- Statistics: Forecast: Forecast model,
- Statistics: Forecast: Forecast model, 4
- Statistics: Forecast: My model
- Statistics: Problems with the study:
- Statistics: Forecasting Controversy
- Summary: State Response Stages and Forecasts
- Protection Features: Treatment Methods (Copy)
- Protection Features: Vaccines (Copy)
- Summary: Hazard Assessment
- Summary: Possible origin: Virus transmission routes: (Copy)
- Summary: Possible origin: Interspecific distribution
- Summary: Hazard assessment: Interspecific distribution
- Summary: Hazard Assessment: Health System Limits
- Summary:Risk assessment: The duration and the «tails»
- Summary: Hazard Assessment: New Year Factor
- Summary: Hazard Assessment: New Year Factor, 2 (Copy)
- Summary: Hazard Assessment: New Year Factor, 3 (Copy)
- Summary: Predictive Models
- Summary: Vaccine Development Probability
- Summary: Vaccine Development Probability
- Summary:Hazard assessment: The impact of the lag on statistics. Effect of incubation period:
- Summary: The effect of the incubation period
- Outcomes: Impact of the incubation period: Assumption of going beyond the SARS level
- Summary: The effect of the window until the authorities react
- Summary: Hazard Assessment: New Year Factor, 2 (Copy)
- Typical misconceptions regarding the virus:
- Summary: Consequences
- Summary: Forecasts and Reality
- Analysis of Probable Influences: The Beginning
- Initial phase: Response: Medics reaction
- Analysis of Probable Influencing Factors: Initial Phase
- Initial phase: Response: Medics reaction, 2
- Initial phase: Response: Reaction of authorities and organizations
- Initial phase: Response: Media response
- Analysis of Probable Influencing Factors: Initial Phase: Assumptions
- Initial phase: Probability: Assumption: The probability of an outbreak starting earlier
- Initial phase: Probability: Proposition No. 1: Total:
- Initial phase: Probability: Proposition No. 1: The main factors influencing statistics
- Internal Factors: Reaction Probability Factors
- Internal Factors: Symptoms
- Internal factors of the statistical system
- Internal factors associated with common indicators
- External factors associated with common indicators
- Internal factors associated with the virus disseminators
- External factors associated with the virus disseminators
- Internal factors associated with the control system
- Summary: Statistics Issues
- Distribution Impact: Summary
- Virus survival: Effect of sunlight activity.
- Virus survival: The effect of water is mainly positive for the virus.
- Summary: Respiratory Filtering Efficiency. (Copy)
- Summary: Why you need to change the mask. (Copy)
- The impact of other measures on the situation
- The impact of other measures on the situation, nose washing, answer to the reader’s question
- Section 2: Factor of virus size, survival and transmission versus all methods
- The effect of other measures on inactivation
- The effect of treatment on inactivation
- The effect of ultraviolet radiation on inactivation, an answer to a reader’s question
- The effect of ozone on inactivation, an answer to a reader’s question
- Section2: Summary: Information about the survivability of the coronavirus on surfaces.
- Probabilities of virus conservation on surfaces: Summary
- Probabilities of virus conservation on surfaces: Summary,2
- Statistics: Learning problems (copy):
- Probabilities of keeping the virus on surfaces without inactivation
- Probabilities of virus conservation on surfaces without inactivation: influence of the main factor
- Section 2: Summary: Virus Potential Viability
- Probabilities of virus conservation on surfaces without inactivation: Summary.
- Summary: Respiratory Filtering Efficiency. (Copy)
- Summary: Why you need to change the mask. (Copy)
- Section 3: Sars Incidence Data (For Comparison)
- SARS Statistics: Cases
- SARS Statistics: Mortality
- SARS Statistics: Mortality by Age
- Section 3: 2019-nCoV incidence data
- Statistics: mortality probability: by age
- Statistics: probability of infection: by age
- Probability statistics for other groups
- Statistics: Cure Probability
- Statistics: death toll (More data in the chart table. From 11.02)
- Statistics: the number of issued
- Statistics: Number of suspicions
- Statistics: number of common cases
- Statistics: number of severe cases
- Statistics: Cumulative cases (More data in the chart table. From 11.02)
- Section 3: Statistics: Country Data
- Section 3: Statistics: Notes and Summary
- Statistics: Results:
- Section 3: Approximate Simple Assessment Scheme
- Statistics: Forecast: Assumptions:
- The characteristics of the coronavirus, including hc, are especially important: Distribution without symptoms (copy)
- The characteristics of the coronavirus, including hc, are especially important: Distribution without symptoms (copy)
- The characteristics of the coronavirus, including hc, are especially important: Distribution without symptoms: Opinion (Copy)
- Summary: Assessment Models for Other Professionals
- Statistics: Forecast: Forecast model, 1
- Statistics: Forecast: Forecast model, 2
- Statistics: Forecast: Forecast model,
- Statistics: Forecast: Forecast model, 4
- Statistics: Forecast: My model
- Statistics: Problems with the study:
- Statistics: Forecasting Controversy
- Summary: State Response Stages and Forecasts
- Protection Features: Treatment Methods (Copy)
- Protection Features: Vaccines (Copy)
- Summary: Hazard Assessment
- Summary: Possible origin: Virus transmission routes: (Copy)
- Summary: Possible origin: Interspecific distribution
- Summary: Hazard assessment: Interspecific distribution
- Summary: Hazard Assessment: Health System Limits
- Summary:Risk assessment: The duration and the «tails»
- Summary: Hazard Assessment: New Year Factor
- Summary: Hazard Assessment: New Year Factor, 2 (Copy)
- Summary: Hazard Assessment: New Year Factor, 3 (Copy)
- Summary: Predictive Models
- Summary: Vaccine Development Probability
- Summary: Vaccine Development Probability
- Summary:Hazard assessment: The impact of the lag on statistics. Effect of incubation period:
- Summary: The effect of the incubation period
- Outcomes: Impact of the incubation period: Assumption of going beyond the SARS level
- Summary: The effect of the window until the authorities react
- Summary: Hazard Assessment: New Year Factor, 2 (Copy)
- Typical misconceptions regarding the virus:
- Summary: Consequences
- Summary: Forecasts and Reality
- Analysis of Probable Influences: The Beginning
- Initial phase: Response: Medics reaction
- Analysis of Probable Influencing Factors: Initial Phase
- Initial phase: Response: Medics reaction, 2
- Initial phase: Response: Reaction of authorities and organizations
- Initial phase: Response: Media response
- Analysis of Probable Influencing Factors: Initial Phase: Assumptions
- Initial phase: Probability: Assumption: The probability of an outbreak starting earlier
- Initial phase: Probability: Proposition No. 1: Total:
- Initial phase: Probability: Proposition No. 1: The main factors influencing statistics
- Internal Factors: Reaction Probability Factors
- Internal Factors: Symptoms
- Internal factors of the statistical system
- Internal factors associated with common indicators
- External factors associated with common indicators
- Internal factors associated with the virus disseminators
- External factors associated with the virus disseminators
- Internal factors associated with the control system
- Summary: Statistics Issues
- Some links
- Updated Charts for 2019-nCov
- News: (Changed)
WHO scientific articles:
1
The full 2019-nCoV genome is now stored online at
GenBank: MN908947.3.
My timeline
Extended Facts: Family
02.02
Coronaviruses are a family of RNA viruses that includes 40 types of viruses in 2 subfamilies as of January 2020. They were named because of the structure of their envelope in the form of a corona.
Coronavirus was first isolated in 1965 in a patient with acute rhinitis. In 2002-2003, the SARS-CoV virus appeared in China. (8000 sick, 800 dead).
In 2012, MERS-CoV. At the end of 2019-beginning of 2020 2019-nCoV. In addition to zoonotic (approx. Causative agents parasitize in the body which is a natural reservoir for them) SARS- and MERS-CoV,
There are four «established» human coronaviruses (HCoV).
Extended Facts: Typology
02.02
2019-nCoV: Kingdom: Riboviria, Type: Incertae Sedis, Order: Nidovirales, Family: Coronaviridae, Genus: etacoronavirus, Subgenus: Sarbecovirus
They are divided into 4 genera, which are called alpha coronavirus, beta coronavirus, gamma coronavirus and deltacoronavirus
1.
HCoV-NL63 and HCoV-229E are alpha-coronaviruses (120-160 nanometers), while HCoV-OC43, HCoV-HKU1, SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, 2019-nCoV are beta-coronaviruses,
1 and
2
Extended Facts: Size
02.02
Viral particles (approx. Virions) are spherical in shape, with some changes in the internal structure (approx. Signs of polymorphism) with a diameter of 75-160 nm (size 2019-nCoV from 60 to 140 / ~ 120 nanometers in diameter).
The height of the protrusions of different coronaviruses is on average 12-24 nm (2019-nCoV 9-12).
Extended Facts: Other
26.01
Different types of coronaviruses infect humans, cats, birds, dogs, cattle, pigs and hares, bats, camels and other animals.
Extended facts: Structure
02.02
Coronaviruses — viruses with a positive RNA chain (+ RNA) in comparison with other RNA viruses have an exceptionally large genome (from thousands of base pairs) and use a complex process strategy (approx. Expression of the genome.),
where hereditary information (DNA nucleotide sequences) is converted to RNA or protein.
They have a polycistronic (approx. Number of sides) genome organization and use a unique transcription mechanism to generate a nested set of subgenomic (sg) mRNAs.
Coronaviruses have a single-stranded RNA genome that encodes 4–5 structural proteins, including the outer membrane protein (N), matrix protein (M), small membrane protein (E), spike (S) glycoprotein (protein), which ensures cell binding and penetration.
Some beta-coronaviruses have a protein (glycoprotein) (HE) that some enveloped viruses use as an invasion mechanism. HE helps in the attachment and destruction of certain sialic acid receptors.
that are on the surface of the host cell…
0.
Symptom Data: Invasion<
02.02
SARS-CoV and the similar 2019-nCoV begins its life cycle by binding its viral particle through a two-component protein (glycoprotein),
which is encoded by the S-segment of the virus genome with the ACE2 receptor on the target cell, and the virus particle is captured by the process of capture of external material by the cell.
Its protein S changes position to facilitate fusion of the endosomal membrane and the release of the RNA genome into the target cell.
After transcription and translation, the viral structural and non-structural proteins and genomic RNA are then assembled into viral particles (approx. The virus is assembled from the components),
Then they are transported through intracellular organelles and released from the target cell.
Symptom Data: Main Symptoms
26.01
Symptoms are generally similar to similar coronaviruses: cough, fever, shortness of breath, chest pain…
The virus is difficult to distinguish from ordinary diseases and it is not always possible to determine the disease with a thermal imager.
02.02?
Irregular cases of signs different from other coronaviruses were recorded at the Wuhan People’s Hospital: Some patients had a poor appetite in the first stages, fatigue, mental problems, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headache. Only after a while did pulmonary pneumonia symptoms begin to be observed.
There is definitely nothing good about the variable characteristics; this may be, in part, a sign of mutability and significant differences in viral samples (polymorphism) or even virus instability.
02.02?
Recently, in the medical journal Lancet, information appeared about the disease of an entire family, including a child.
This is the first such case. Scientists have found very high infectiousness of the virus, the chance of infection with the proximity of the diseased is high.
Similar signs of three coronaviruses
28.01?
Scientists have confirmed that coronavirus belongs to the same group of viruses as the causative agent of SARS-CoV SARS, as well as the strain of Middle East respiratory syndrome MERS-CoV. Hundreds of people died from diseases caused by these viruses.
The 2019-nCoV genome is very similar to the already known coronaviruses. It's RNA most (96.2% nucleotide coincidence) was similar to the RNA of a virus similar to the SARS virus found a couple of years ago in bats Rhinolophus affinis in Yunan Province.
According to other studies, the 2019-nCoV gene is 79.5% identical to SARS-CoV SARS RNA. It retained one of its five sites.
He also has the same receptor (ACE2).
However, there is a high probability that the new virus differs from SARS and from the bat virus, including mortality (-) and transmission rate (+), more about this below.
Gaps in understanding coronavirus source
26.01
There is a significant chance that scientists do not yet fully understand the nature of the 2019-nCoV coronavirus, or even make mistakes again, as was the case with the hCoV-EMC virus detected in 2012.
One case from the past ,1
At that time, it was also suggested that hCoV-EMC and SARS had the same infection pathway, but this was not confirmed after studies.
In 2012, as a result of studies at the University of Bonn Medical Center at modifying hamster kidney cells, scientists forced them to produce ACE2 human receptors.
SARS-coronavirus was able to enter these cells, but hCoV-EMC did not succeed — this proves that the hCoV-EMC virus does not need ACE2 receptors to enter the cell.
What is most interesting, then it was not possible to establish which receptors are needed by hCoV-EMC.
One case from the past ,2
26.01
Also, a signal that scientists still do not fully understand the origin of the virus can be a recent statement that the current virus was transmitted from snakes, which many scientists consider unlikely.
Nature magazine published commentaries by leading virologists from around the world stating that snakes could hardly have been the source of a new coronavirus.
Establish which receptors are needed by hCoV-EMC.
Understanding Gaps: Probably Wrong Hypotheses
28.01
There is a hypothesis that the 2019-nCoV virus was obtained in the laboratory from the Wuhan Institute of Virology. (approx. Then there were scientific articles hinting at this; see paragraphs Understanding spaces: Probable medium, studies, 2 and 3)
However, I believe such hypotheses are not yet sufficiently substantiated.
Understanding Gaps: A Possible Carrier, Research
28.01
Another group of researchers at the Wuhan Institute believe that the most likely carrier of coronavirus 2019-nCoV was a bat.
Moreover, most likely this virus is a hybrid of another coronavirus. They believe that this coronavirus is very similar to the one that occurred in 2003 (SARS).
Later, Xinguan Li and his colleagues from Wuhan University of Bioengineering recently suggested the sequencing of the 2019-nCoV genomes and other coronaviruses,
that the causative agent of the current epidemic arose as a result of the hybridization of the viruses of bats and snakes, and another group of scientists came to other conclusions.
Understanding Gaps: A Probable Virus Carrier, Research,1
28.01
There was a study indicating that the region of the receptor binding domain of the S gene was taken from the ZS bat-CoV virus (80% similarity).
This is a new virus with a more efficient receptor binding domain.
Understanding Gaps: A Probable Virus Carrier, Research,2<
28.01
 Some people had no connection with the market
Some people had no connection with the market
The initial hypothesis about the origin of the virus through the Wuhan market may not be entirely true. Details were described as the first 41 hospitalized patients in whom the new 2019-nCoV coronavirus was confirmed.
According to researchers, 13 out of 41 cases had no connection with the seafood market.
Researchers isolated the virus from the fluid obtained from the bronchi of patients, sequenced the RNA found there. These actions were carried out on five more patients.
That allows 2019-nCoV to be considered a snake virus, scientists have not found.
Understanding Gaps: A Probable Virus Carrier, Research,2
28.01?
It was found that the entry point of the 2019-nCoV virus into the human or animal organism is the same as in the case of the SARS SARS virus — ACE2 receptors.
The virus joins them with its suction cups and then injects its RNA into the cell.
Receptors are located in cells located deep in the lungs. SARS discovered in 2003 the method of penetration through ACE2, this makes the new coronavirus and SARS very similar.
The difference in the genome of different samples of the virus is very small, which indicates that the hybrid virus appeared no earlier than the end of October 2019.
Gaps in understanding the coronavirus Source: A study that was conducted hCoV-EMC
28.01
In a typical case, a typical coronavirus that comes from bats is transmitted to another animal species or person, it ceases to infect bat cells.
In the case of hCoV-EMC, he continued to do so, as was proven by the center.
Gaps in understanding:Summary
26.01
The most likely options are: hybridization with an unknown virus. Hybridization of viruses from a bat and a snake. More research is needed.
It is necessary to carry out work to refute some of the speculative theories.
Coronavirus most likely crossed the cross-species barrier to humans, most likely, through the intermediate link — a domestic or wild mammal (for example, MERS passed from bats through one-humped camels, and SARS through presumably vivver). Beta-cononaviruses are found only in mammals, including humans. Therefore, many do not believe in the option of snakes.
Features of coronavirus, including especially important.
TODO: Добавить новую главу в течении 1-7 дней.
Features of coronavirus: Incubation period
29.01?
The incubation period can reach 14 days.
Possible origin: Virus transmission methods: Contagiousness (Copy)
04.02
There is information about the high infectivity of the virus during the incubation period. (From 2.0 to 4.0) This was stated at a press conference in Beijing by the Head of the State Committee for Healthcare of China Ma Jiaovei.
Some experts do not believe about the contagiousness of the virus during the incubation period.
“I seriously doubt that Chinese government officials have any evidence to support this claim. “I don’t know any evidence that over 17 years of working with SARS and MERS coronaviruses (they often compare the new coronavirus 2019-nCoV with them — ed.), It was discovered that someone got infected during the incubation period,” said Michael Osterholm, Director of the Center for Research and Policy on Infectious Diseases at the University of Minnesota.
Possible origin:
26.01-28.01
Now we can assume several options:
Origin from bats and an unknown animal like the hCoV-EMC coronavirus or bats and snakes. In the second case, this is a unique case, since it is a transmission from cold-blooded, albeit partial.
Perhaps the infected bats hit the market in Wuhan, where they sell them, including for cooking in the form of soup, a local delicacy.
Markets such as the Wuhan fish market (where they sell different kinds of animals) are a haven for the spread of coronavirus, like the current one or what happened in 2003 (SARS). So the emergence of a new virus was only a matter of time. Some virologists regularly reminded of this.
Possible origin: Summary:required actions
26.01-28.01
Despite these reports, there are several important signs, most likely not taken into account, that could shed light on the characteristics of the virus.
For example: research is needed on the likelihood of a virus surviving in an environment outside the body, as well as studies on the interspecific transmission of the virus as was done with hCoV-EMC.
Thus, it would be nice to conduct a study on this topic, to conduct a similar experiment with a new coronavirus. So you can see other features of the new virus.
Possible origin:Summary:Suspicion<
26.01-28.01
If my suspicion is confirmed, then the new coronavirus has at least several variants of the disease vector:
humans, pigs and some species of bats. This is very bad since it is not known whether the authorities take this problem into account.
In addition, the high probability of mutations of this virus can be dangerous and can lead to the appearance of an easily passing interspecific barrier, a “universal” virus.
By removing the dependence of the virus on a particular receptor or by increasing the number of possible methods of infection, such a virus can be obtained.
Sooner or later, similar coronaviruses may appear, which can be very disastrous
Possible origin: Methods of spreading the virus
04.02
The bulk of the spread is airborne. Up to 100 million genomes per ml are found in nasopharyngeal secretions.
In 32% of cases in patients, on average, 3.2 days after the onset of the disease and in 68% on day 14
Viral RNA was detected in stool samples in 97% of patients 2 weeks after illness and in 42% of urine tests.
Fecal-oral transmission is strongly suspected.
1.
Possible origin: Virus transmission methods: Contagiousness (Copy)
04.02
There is information about the high infectivity of the virus during the incubation period. This was stated at a press conference in Beijing by the Head of the State Committee for Healthcare of the People's Republic of China, Ma Jiaovei.
Some experts do not believe the contagiousness of the virus during the incubation period.
“I seriously doubt that Chinese government officials have any evidence to support this claim. “I don’t know any evidence that over 17 years of working with SARS and MERS coronaviruses (they often compare the new coronavirus 2019-nCoV with themed.), It was discovered that someone got infected during the incubation period,” said Michael Osterholm, Director of the Center for Research and Policy on Infectious Diseases at the University of Minnesota.
This section contains information on the protection and survival of the virus. Next Section: Statistics
Section 2: A Brief History of Medical Remedies
At the beginning of the XVII century, French physician Charles Lorm created a suit that was supposed to protect doctors from illness, created a suit for «plague doctors»
Composition of the plague doctor’s suit: Thick waxed coat, gloves, hat with brim, “crow” mask, which covered the whole face.
The nose of the mask was stuffed with hay, dried herbs (lavender, mint, cloves and so on), spices, camphor or laid with a sponge dipped in vinegar.
At that time, it was believed that the disease was caused by odors (miasma), so the mask was created to drive away from the smell but actually acted as a respirator.
The openings for the eyes in the mask were covered with glass, and the “plague doctor” himself interacted with the patient or the deceased mainly with a cane.
In the 1860s, the famous hygienic physician Joseph Listerov created the theory of antiseptics. Since that time, more attention has been paid to the protective medical “uniform.” The doctor’s white coat was introduced in the second half of the 19th century. Rubber gloves for protecting hands appeared in 1886 at a US military hospital.
A gauze-watt bandage appeared only in 1916-18 — as a protection against the Spanish epidemic. Already in the 20-30s, masks were required to be worn by medical personnel.
Section 2: Features of protection against the virus: Treatment and prevention
Protection Features: Treatment
26.01-28.01
ВОЗ не рекомендует какие-либо конкретные меры по лечению болезни дома. В случае симптомов рекомендуется обратиться за медицинской помощью.
04.02
It is possible that rather toxic ribavirin may be effective, which in itself has a teratogenic effect (can cause fetal malformations) and can lead to death due to suppression of blood formation. Therefore, it is impossible for pregnant women and the use is strictly under the supervision of a doctor. He has shown beneficial effects on SARS. In any case, it should not be used due to toxicity.
Protection Features: Treatment Methods (Copy)
27.01-01.02TODO: Добавить методы лечения
There are methods that can alleviate the most dangerous symptoms of the virus:
It is now known that as a temporary measure to reduce the symptoms of coronavirus, Chinese patients are treated with two HIV drugs — a combination of lopinavir and ritonavir, writes Bloomberg. No effective antiviral drugs against the virus exist today.
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (EXMO) — oxygen saturation of the blood makes it possible to survive the most dangerous symptoms.
Protection features: Treatment methods. Question from the reader: Effect of ACE2 blockers
27.01-01.02TODO: Добавить методы лечения
Hi, I wanted to ask if COVID19 penetrates ACE2
can blockers of this enzyme help for treatment?
e.g. Lozatran yandex.ru/health/pills/product/lozartan-teva-29982/prices
Yes, they can help in the treatment, alleviation of symptoms.
1 and
1 . Results only in clinical cases.
However, the result will depend on the specific inhibitor, so some drugs can inhibit coronavirus only in words. Thus, such treatment is possible only in a hospital and with an already approved, tested inhibitor.
There are many variants of inhibitors that inhibit the virus in one way or another. And there are also many ways to do this.
Protection Features: Vaccines (Copy)
27.01-01.02
Now scientists are testing, including previously manufactured vaccines, intended for other coronaviruses at 2019-nCoV, as just stated
Head of the Center for Disease Control and Prevention Xu Wenbo.
Another scientist is trying to enter the country and test samples. Success can make a difference. Otherwise, the vaccine will have to wait a very long time, up to several years.
The US and Russia are already developing the first vaccine options. A certain result is possible in a few months. Research and development are ongoing for MERS-CoV.
1/28/06/02?
Researchers at the University of Hong Kong said they had developed the 2019-nCoV coronavirus vaccine, which already killed 132 people. The team modified the conventional flu vaccine and added part of the 2019-nCoV coronavirus surface antigen to it. The authors believe that the vaccine will protect against both the flu and the Chinese coronavirus.
Doctors at the Rajawiti Hospital in Bangkok say a new approach to coronavirus treatment has improved several patients. According to unconfirmed information: oseltamivir + Lopinavir + Ritonavir.
The Thai Ministry of Health will have a discussion on Monday about this. The doctor accidentally increased the dose of one of the drugs.
Now the approach is used only in severe cases. It is too early to talk about the universality of this approach and it is not worth buying these drugs in the hope of self-medication. If this approach is confirmed in the world, it will be an additional opportunity to save patients and will be used in practice.
01/29/20120
The good news: Attempts to use all possible combinations have had their effect.
The good news: One of the antibodies that was created against the SARS epidemic of 17 years ago is able to neutralize the coronavirus of the new strain.
bioRxiv has material on this subject.
This refers to the CR3022 molecule, which is effective against the SARS virus. Scientists have determined that this antibody also actively joins the 2019-nCoV virus.
Other antibodies that are much more effective than CR3022 do not respond at all to 2019-nCoV. They target ACE2 ribosome binding sites. These antibodies could not bind the 2019-nCoV spike protein,
Coronaviruses are attached to cell receptors using a spike protein. This triggers changes in the structure of the spike protein and leads to fusion between the viral and cell membranes.
This indicates that the difference in the receptor-binding domain (RBD) region of SARS-CoV and 2019-nCoV has a critical effect on the cross-reactivity of neutralizing antibodies, and that it is still necessary to develop new antibody-targeted antibodies produced by immune cells belonging to one cell clone that could specifically bind to 2019-nCoV RBD.
Information on the specific structure of the receptor-binding domain is also confirmed in another study. Read more at:
Receptor binding domain as a target for the development of SARS vaccines.
Biologists believe that the use of CR3022 in combination with other substances «compatible» with the 2019 pathogen makes it possible to quickly synthesize the first drugs.
The good news: Australia has announced the successful creation of a laboratory version of the Chinese coronavirus.
02/01/20120
Researchers at the University of Hong Kong said they had developed the 2019-nCoV coronavirus vaccine. The team modified the conventional flu vaccine and added part of the 2019-nCoV coronavirus surface antigen to it. The authors believe that the vaccine will protect against both the flu and the Chinese coronavirus.
Unfortunately there is no more specific information.
03.02 2020
In Thailand, cases of cure patients were recorded using a combination of drugs. According to some reports: Oseltamivir (dosage was increased) + Lopinavir + Ritonavir. It is too early to talk about the full use of this method around the world. A meeting will be held at the Thai Ministry of Health on Monday. A possible application of the method will be discussed there.
Do not try to use a similar combination at home.
So far, the necessary studies on the effectiveness of the triple combination in such a dosage have not been carried out. The drugs have many side effects, some of which are severe, in addition, the drugs are quite expensive.
Even doctors use this option only in the most severe cases.
A similar combination has already been used in medical practice incl. separately
04.02 2020
GeoVax, a biotechnology company, has signed a letter of intent with BravoVax, a vaccine developer based in Wuhan, China, to jointly develop a coronavirus vaccine using the 2019-nCoV genetic sequences.
Inovio Pharmaceuticals is partnering with Beijing-based Advaccine Biotechnology to advance the development of the INO-4800 vaccine. The vaccine is a potential treatment for 2019-nCOV.
Clover Biopharmaceuticals is developing a recombinant subunit vaccine using patented Trimer-Tag technology. The company is developing a vaccine based on the S-Trimer protein of the 2019-nCoV virus, which is responsible for binding to the host cell and causing viral infection.
Vaxart is developing an oral recombinant tablet vaccine using its own VAAST oral vaccine platform.
CytoDyn considers Leronlimab (PRO 140). The drug is already in the second phase of clinical trials as a treatment for HIV.
Remdesivir (GS-5734): China has filed a new patent for a drug created by Gilead Sciences Inc., which, according to its scientists, can fight against coronavirus.
Biocryst Pharma Halidesivir (BCX4430) is a Potential Antiviral for Coronavirus
Section 2: Features of the virus protection: masks: Pros and Cons
Why WHO, other doctors do not recommend the use of masks. Why you can still use them
Cons of PPE
16.02
Usually referring to medical masks and not respirators. The effectiveness of medical masks is only if most people use them, or patients wear them to prevent the spread of the virus.
Cause a shortage of masks and respirators for doctors.
Some manufacturers warm their hands on masks. Some protective equipment can be quite expensive.
It is necessary to change or inactivate the virus on masks and respirators.
The difficulty of inactivating (destroying) the virus in masks and respirators.
You may forget to inactivate masks. It is necessary to keep personal statistics and control.
It may be necessary to understand the characteristics of the survivability of the virus and its inactivation (below in the article), to have the appropriate reagents and equipment.
Pros of PPE
16.02
There are a large number of cheap and completely reliable respirators until they are sold out.
The effectiveness of the respirators of the corresponding categories has been proved (in more detail below).
You can effectively protect yourself if you strictly follow the instructions.
Section 2: Features of the virus protection: masks: Features
Protection Features: Masks: If
26.01-28.01
If the virus is transmitted through the lung receptors (ACE2), it is likely that the virus is most likely to pass through the breath, the virus has not mutated, is not similar to hCoV-EMC.
Protection Features: Masks: Disadvantages
26.01-28.01
Conventional medical masks are an inadequate means of protection, especially if they become wet,
in addition, they must be regularly changed, which is usually ignored (especially in conditions of shortage or high prices for them, the press reports that a strong increase in the price of PPE is reported)
Conventional masks are ineffective. There are risks of infection through open eyes and the conjunctiva.
In addition, the unconscious habit of touching the face of many also does not contribute to protection. Therefore, fully enclosed gas masks, respirators are preferable.
The very ratio of the size of the virus to the fibers of the dressings is also not optimistic. Other scientists also consider respirators to be necessary.
More details above in the paragraph Cons of PPE and Pros of PPE.
Summary: Respirators can be used.
Therefore, it is quite possible to use respirators. You can quite effectively protect yourself if you strictly follow the instructions.
In any case, you should not risk it: use gloves and cover any skin areas with clothes or glasses in the absence of protective clothing.
Protection Features: Masks: Best Option
26.01-28.01
Therefore, it is better to use gas masks or respirators with glasses, as a means of protection, devoid of the shortcomings of medical masks and light respirators.
The WHO publication disease-commodity-package states the requirements for a respirator:
It is made of transparent plastic and provides good visibility for both the medical worker and the patient, the adjustable tape should fit snugly to the head and fit snugly to the forehead, resistant to fog (preferably), completely cover the face, can be reusable (made of durable material that can be cleaned and sanitized) or disposable.
- standard directive ЕС 86/686 / EEC, EN 166/2002,
- ANSI / ISEA Z87.1-2010
- or equivalent
In other sources: not lower than N95with a HEPA filter. According to Russian standards, the analogue of N95 will be FFP2, N99 — FFP3. Thanks @ Alyoshka1976 remark.
You can read about Respiratory Protection and Disinfection:
Respiratory Protection and Disinfection FAQ.
Respiratory Protection and Disinfection.
Section 2: Features of virus protection: conventional mask: Research
Concerning more specific data: A couple of studies were conducted on the effectiveness of masks, most of which were field studies,
examined groups of patients on the effectiveness of measures. Check out:
1 and
2
A prospective cluster-randomized study was done that compared surgical masks, unverified P2 masks, and the absence of masks
in the prevention of influenza-like diseases (ILI) in households. It has been found that adherence to the mask significantly reduces the risk of infection with ILI,
but <50% of participants wore masks most of the time.
It was concluded that the use of face masks However, during a severe pandemic, when the use of face masks may be more
the spread of the pandemic in households can be reduced. Thus, the efficiency will increase with the number of% of mask carriers.
Virus survival: The effect of water is mostly positive for the virus. (Copy)
04.02
Water, a frequent means of transmitting viruses, can contribute to their survival, but many environmental factors will adversely affect the virus population.
Keeping the dressing wet can help the virus survive.
One study on water:
A study of the survival of a typical virus in the aquatic environment
There are suggestions that the environment that forms after a certain time in masks contributes to the conservation of viruses for a longer time.
Because of this, there is a certain risk of infection by touching the mask and carrying the virus.
Summary: Respiratory Filtering Efficiency. (Copy)
04.02
Filtration efficiency of individual face filter respirators (FFR) and NIOSH approved N95 and P100 particulate filter cartridges,
has been tested against viable MS2 virus, a non-pathogenic bacteriophage aerosolized from a liquid suspension. Its size (23-28 nanometers)
The tests were carried out under two cyclic flow conditions (minute volumes 85 and 135 l / min) and two constant flow rates (85 and 270 l / min).
The average penetration of viable MS2 through FFR / N95 and P100 cartridges was typically less than 2 and 0.03%, respectively, under all flow conditions.
Given that the minimum samples of coronaviruses exceed the size of MS2 at least 40-60nm.
An acceptable safety margin for respirators FFP2 and N95 can be stated with a good face seal.
A particle filter respirator N99 (FFP3) filters at least 99% of the particles in the air, but is not oil resistant.
1
Section 2: Host Coronavirus Adaptability
16.02
In simple words, the paragraph below can be explained as follows: The virus can adapt to the host, has some tricky mechanisms, it was not difficult for him to cross the border between animals and humans.
Virus Survival: Adaptability of the Virus.
04.02
Many of the coronavirus proteins expressed in the infected cell promote the interaction of the coronavirus with the host.
For example, by interacting with the host cell to create the optimal environment for replication of coronavirus,
by altering the expression of the host gene or counteracting the antiviral defense of the host.
Many of these interactions affect the outcome of the infection, including adaptation and cross-species crossing.
Virus survival: Interspecific transition
04.02
The number of mutations in the receptor-binding domain of the SARS-CoV spike (S) protein; the interspecific limit for the transition was insignificant.
1.
Li et al. 2005c (см. Главу 2). .
Chemicals that inhibit or delay the physicochemical processes of peptidases do not affect the penetration of the virus.
This indicates that the use and penetration of the SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV receptors and, therefore, 2019-nCoV are independent of the activity of the peptidase receptor.
They depend only on binding to these specific host receptors.
1.
Section 2: Introductory information on the survivability of viruses.
In the absence of host cells, viral populations in the environment can only decrease or remain stable.
Evaluation and analysis of the shape and intensity of this reduction represent the main objectives of viral inactivation studies.
Virus survival: Effect of temperature, a key factor.
04.02
An increase in temperature is the main factor influencing the survival of the virus in the environment through protein denaturation,
nucleic acid damage or decay of the outer envelope of the virus (capsid)
Inactivation mechanism
Higher temperatures mean faster inactivation of the virus. At low temperatures above zero, viruses can survive for long periods of time, often longer than the duration of the study.
Cold Survival
At higher temperatures, the viral population will be reduced by several orders of magnitude over several days.
Decreasing the population at higher temperatures
The freezing temperature allows viruses to remain stable for at least a couple of months, but in the early days, an initial decrease can be observed.
Virus survival at temperatures below zero.
A minimal decrease in infectivity was found after 21 days at 4 degrees Celsius. Heating to 56 ° C inactivates the coronavirus quickly.
1 .
SARS-Cov is stable in feces and urine at room temperature for at least 1-2 days, especially if diarrhea is present (high pH);
Virus survival: Question from the reader..
04.02
There is a question about heating in the
Neuromantix building:
0 about heating in the building.
0 The results indicate that additional calculations of the correlation of relative humidity and different temperatures are needed.
It is too difficult to choose the optimal ratio of temperature and humidity at home. An increase in temperature gives a better result in most cases.
Most likely there are no practical studies to increase the temperature in the room as a factor in reducing risks.
However, based on the temperature information, you can try to increase the temperature. Humidity can be chosen to taste.
However, it is impossible to fully defend yourself in this way.
0
To ensure a high rate of inactivation of the virus, it is necessary to provide a greater temperature than 28-30 degrees.
Virus survival: Humidity, an additional factor.
04.02
The relationship between inactivation and relative humidity is not monotonous, there was a higher survival rate or a higher protective effect at low relative humidity (20%)
and high relative humidity (80%) than with moderate relative humidity (50%). There was also evidence of the interaction between AT and RH.
0
Virus Survival: Effect of Temperature, Key Factor. (Copy)
Virus survival was increased by lowering AT (temperature). A similar relationship between AT and virus inactivation was observed for enveloped viruses in liquids and aerosols.
The coronavirus data obtained in this study suggest that although viral inactivation rates are lower at lower antibodies,
nevertheless, the effects of REs on the survival of viruses at each AT are different.
With surrounding ATs (around 20 ° C), coronaviruses can survive for 2 days, losing only 1–2 log 10 of infectivity, depending on relative humidity.
With decreasing temperature, the survival of the virus will rise. The virus can survive weeks at a temperature of -1.
Distribution Impact: Summary
04.02
The bulk of the spread is airborne. Up to 100 million genomes per ml are found in nasopharyngeal secretions.
In 32% of cases in patients, on average, 3.2 days after the onset of the disease and in 68% on day 14
Viral RNA was detected in stool samples in 97% of patients 2 weeks after illness and in 42% of urine tests.
In order to get infected, you usually need to be within a certain radius (usually 1.5-2 m) from the infected.
Perhaps the influence of a genetic predisposition and characteristics as in vulnerable groups (for example, lowered immunity).
Either (contact) to transfer viral particles from objects, or direct contact with mucous surfaces.
Fecal-oral transmission is strongly suspected.
1 .
My opinion: I can say that uniformity of infection is almost impossible. There are situations with a positive opportunity for the virus to spread, and vice versa.
«Positive» situations are much less than negative. Therefore, all these models can do little.
Virus survival: Effect of sunlight activity.
04.02
Sunlight is another important factor causing viral inactivation by ultraviolet radiation.
The presence of an indigenous microbial population negatively affects the survival of the virus.
The presence of organic matter in water has a positive effect on the survival of the virus. Other factors responsible for increased viral inactivation,
include the presence of disinfectants.
Sunlight activity can be explained by damage to nucleic acids through the formation of pyrimidine dimers or other products,
other mechanisms may be involved, such as the excitation of active substances present in the outer shell of viruses or in the environment.
Virus survival: The effect of water is mainly positive for the virus.
04.02
Water, a frequent means of transmitting viruses, can contribute to their survival, but many environmental factors will adversely affect the virus population.
Keeping the dressing wet can help the virus survive.
One study on water:
A study of the survival of a typical virus in the aquatic environment
Summary: Respiratory Filtering Efficiency. (Copy
04.02
Filtration efficiency of individual face filter respirators (FFR) and NIOSH approved N95 and P100 particulate filter cartridges,
has been tested against viable MS2 virus, a non-pathogenic bacteriophage aerosolized from a liquid suspension. Its size (23-28 nanometers)
The tests were carried out under two cyclic flow conditions (minute volumes 85 and 135 l / min) and two constant flow rates (85 and 270 l / min).
The average penetration of viable MS2 through FFR / N95 and P100 cartridges was typically less than 2 and 0.03%, respectively, under all flow conditions.
Given that the minimum samples of coronaviruses exceed the size of MS2 at least 40-60nm.
An acceptable safety margin for respirators FFP2 and N95 can be stated with a good face seal.
A particle filter respirator N99 (FFP3) filters at least 99% of the particles in the air, but is not oil resistant.
1
Summary: Why you need to change the mask. (Copy)
04.02
Over time, the protective capabilities of respirators degrade.
There are suggestions that the environment that forms after a certain time in masks contributes to the conservation of viruses for a longer time.
Because of this, there is a certain risk of infection by touching the mask and carrying the virus.
There is a Ukrainian scientific article for filtering respirators. The value of degradation is indicated.
1
Therefore, PPI inactivation methods are important. FAQ on respiratory protection and disinfection.
Otherwise, one could not change the mask and not inactivate the viral particles on the protective equipment. Virus RNA can exist on objects for a very long time. The protective capabilities of PPE are not permanent. After a certain time, depending on the protection class, etc. they exhaust their margin of safety. After this, the transfer of viral particles from protective equipment is possible.
So there are two options: to extend the service life (including inactivating PPE) or change them.
The number of bacteria on the surface of the mask increases with increasing operating time; a significant difference was found between 4-6-hour and 0-hour groups (p <0.05).
1.Replacement of masks is necessary due to the factor of a drop in the quality of antibacterial protection.For example, here is the degradation of static charge:
1,
2
It is likely that coronavirus retention time will increase on breath-heated and moist dressings. Practical studies are needed.
Probably the features for inactivating 2019-nCoV are generally similar to SARS, but I would like to see real practical research on this.
The factor of preservation of the virus in an open environment may be another unaccounted factor affecting the spread of the virus.
Water, a frequent means of transmitting viruses, can contribute to their survival, but many environmental factors will adversely affect the virus population.
Keeping the dressing wet can help the virus survive.:
A study of the survival of a typical virus in the aquatic environment
Regarding more specific data: A couple of studies were conducted on the effectiveness of masks, and most of them were field studies, and groups of patients were examined for the effectiveness of the measures.
Check out:
1 and
2
The impact of other measures on the situation
04.02
Evaluation of other measures: school closure
1 and randomized controlled handwash studies
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9,
10
The impact of other measures on the situation, nose washing, answer to the reader’s question
04.02
There is not much information on nasal irrigation (rinsing the nose).
1
Naturally, there is no information on 2019-nСov or SARS. Conducting such studies is very difficult. There are a large number of washing methods. Not all of them have been investigated.
1
Significant improvements have been made in the control group. This may be suitable as an additional method of risk reduction in addition to hand washing and other methods.
However, each exit from the house becomes a whole mission and it will be difficult to keep track of everything.
Virus survival: The effect of water is mainly positive for the virus.
SARS data are presented. Given the similar characteristics of coronaviruses (differences appear, for example, in the receptor-binding domain (RBD)), the situation can be reliably predicted.
The effect of other measures on inactivation
04.02
Other factors responsible for enhancing viral inactivation include the presence of disinfectants such as chlorine
1,
2,
1,
1, extreme pH
1,
1,copper
1 or aeration. Some factors, such as water hardness, are less reliable.
1
The effect of treatment on inactivation
04.02

The relatively large size of 2019-nCoV (~ 29.9 thousand base pairs and an average of 120 nm, min 60) and the lipid membrane make it susceptible to stages with virus inactivation, including used during production processes,
such as surfactants, solvents (S / D)
1 , waste management (low pH incubation), use of caprylate, pasteurization
1
or heat treatment,
1 ,
2 ,
nanofiltration or fractionation processes… The effectiveness of these processes has been demonstrated on other model lipid-coated viruses, which are very similar to 2019 nCoV, for example, human coronavirus 229E and OC43, SARS-CoV and porcine coronavirus TGEV.
The effect of ultraviolet radiation on inactivation, an answer to a reader’s question
04.02
Based on
1 and
1 SARS was inactivated by ultraviolet light (UV) at 254 nm,
heat treatment at 65 ° C or more, alkaline (pH> 12) or acid (pH <3) conditions, treatment with formalin and glutaraldehyde.
Liquid samples of bovine plasma did not contain detectable viable PPV after 15 minutes of exposure (cumulative UV-C irradiation of 2295 J / l)
1
The bad news is the SARS-like virus (2019-nCov) is inactivated for a period of at least 15 minutes at 56 degrees or 254 nm. Better than 20 minutes at 254 nm. This worsens the effects. Not every time you want to spend so much time.
1 With a shorter time, the probability of the survival of viral particles increases. virus inactivation with little information.
The effect of ozone on inactivation, an answer to a reader’s question
05.02
The proportion of live viruses on the surface decreased exponentially with increasing doses of ozone.
0 .
Viruses needed ozone doses of 20-112 min (mg / m3) (contact time [min] multiplied by the ozone concentration [mg / m3) for 90% inactivation and 47-223 min (mg / m3) for 99% inactivation.
The ozone dose for inactivation of 99% was two times higher than for inactivation of 90%. The required ozone concentration at a relative humidity of 85% was lower than at a relative humidity of 55%.
Section2: Summary: Information about the survivability of the coronavirus on surfaces.
Given the basics of the theory presented in the previous paragraph, we can try to predict the features of the survival of the virus outside the body.
Based on the data, you can be more or less confident in a sufficient margin of safety compared to 2019-nCoV.
SARS-Cov virus particles are sensitive to treatment with lipid solvents, nonionic detergents, oxidizing agents;
Probabilities of virus conservation on surfaces: Summary
04.02
In a scientific article, environmental surfaces were recognized as probable factors,
contributing to the transmission of nosocomial viral infections
1 .
The question of whether hospital surfaces play a role in the spread of nosocomial viral infection has become particularly relevant in connection with recent news.
Probabilities of virus conservation on surfaces: Summary,2
04.02
During SARS Coronavirus Outbreak (SARS-CoV), SARS-CoV nucleic acids were detected on surfaces and inanimate objects
0 ,
0
It is likely that surfaces can be sources of virus transmission. Risk assessment requires data on inactivation of the virus on environmental surfaces and data on
how environmental inactivation affects the inactivation of the virus, such as air temperature (AT) and relative humidity (RH), and more.
Statistics: Learning problems (copy):
04.02
Due to the fact that the study of the most dangerous coronaviruses requires specially trained personnel working in laboratory conditions of biosafety level 3 (BSL-3) or 4,
there are big problems in the study of this virus, and only limited data are available on the survival of the coronavirus and the response to stressful environmental factors.
The results show that when large quantities of surrogates are deposited, these viruses can persist for several days on surfaces in the AT environment and
in a wide range of relative humidity levels (from 20 to 60% relative humidity) typical of healthcare environments.
Probabilities of keeping the virus on surfaces without inactivation
04.02
Coronavirus may be more resistant to surface inactivation than previously studied human coronaviruses. SARS-CoV was reported to survive for 36 hours on stainless steel
0 However, the AT and RH conditions were not presented for the previous experiment, which makes comparison difficult.
Rabenau et al.
0 reported a much slower inactivation of SARS-CoV on the polystyrene surface
(decrease of 4 log 10 after 9 days; AT and RH conditions were not reported)
which is consistent with some observations of TGEV and MHV
Probabilities of virus conservation on surfaces without inactivation: influence of the main factor
04.02
Virus survival was increased by lowering AT (temperature). A similar relationship between AT and virus inactivation was observed for enveloped viruses in liquids and aerosols.
The coronavirus data obtained in this study suggest that although viral inactivation rates are lower at lower antibodies,
nevertheless, the effects of REs on the survival of viruses at each AT are different.
With surrounding ATs (around 20 ° C), coronaviruses can survive for 2 days, losing only 1–2 log 10 of infectivity, depending on relative humidity.
With decreasing temperature, the survival of the virus will rise. The virus can survive weeks at a temperature of -1.
Section 2: Summary: Virus Potential Viability
Probabilities of virus conservation on surfaces without inactivation: Summary.
04.02
Based on survival data, it can be assumed that enveloped viruses can remain infectious on surfaces for a long time,
so that people can come into contact with them, which creates a risk of infection, which leads to infection and possible transmission of the disease.
Summary: Respiratory Filtering Efficiency. (Copy)
04.02
Filtration efficiency of individual face filter respirators (FFR) and NIOSH approved N95 and P100 particulate filter cartridges,
has been tested against viable MS2 virus, a non-pathogenic bacteriophage aerosolized from a liquid suspension. Its size (23-28 nanometers)
The tests were carried out under two cyclic flow conditions (minute volumes 85 and 135 l / min) and two constant flow rates (85 and 270 l / min).
The average penetration of viable MS2 through FFR / N95 and P100 cartridges was typically less than 2 and 0.03%, respectively, under all flow conditions.
Given that the minimum samples of coronaviruses exceed the size of MS2 at least 40-60nm.
An acceptable safety margin for respirators FFP2 and N95 can be stated with a good face seal.
A particle filter respirator N99 (FFP3) filters at least 99% of the particles in the air, but is not oil resistant.
1
Summary: Why you need to change the mask. (Copy)
04.02 Todo: Добавить больше примеров, добавить основной аргумент в коментах
Over time, the protective capabilities of respirators degrade.
There are suggestions that the environment that forms after a certain time in masks contributes to the conservation of viruses for a longer time.
Because of this, there is a certain risk of infection by touching the mask and carrying the virus.
There is a Ukrainian scientific article for filtering respirators. The value of degradation is indicated.
1
This is not related to viruses, but the number of bacteria on the surface of the mask increases with increasing operating time; a significant difference was found between 4-6-hour and 0-hour groups (p <0.05).
1. Replacement of masks is necessary due to the factor of a drop in the quality of antibacterial protection.
For example, here is the degradation of static charge:
1,
2
It is likely that coronavirus retention time will increase on breath-heated and moist dressings. Practical studies are needed.
Probably the features for inactivating 2019-nCoV are generally similar to SARS, but I would like to see real practical research on this.
The factor of preservation of the virus in an open environment may be another unaccounted factor affecting the spread of the virus.
Water, a frequent means of transmitting viruses, can contribute to their survival, but many environmental factors will adversely affect the virus population.
Keeping the dressing wet can help the virus survive. One such study:
A study of the survival of a typical virus in the aquatic environment
Regarding more specific data: A couple of studies were conducted on the effectiveness of masks, and most of them were field studies, and groups of patients were examined for the effectiveness of the measures.
Check out:
1 and
2
Section 3: Sars Incidence Data (For Comparison
26.01-28.01 TODO: Обновить всю статистику
SARS Statistics: Cases
26.01-28.01
in 2003, 8437 cases of the disease were noted, of which 813 were fatal. Undoubtedly, 2019-nCoV is the leader in the number of infected among coronaviruses causing severe respiratory syndrome.
From coronaviruses known from the 60s with milder consequences, much more fell ill.
SARS Statistics: Mortality
26.01-28.01
In 2003 (SARS), about 9% of patients with a confirmed diagnosis died. Now mortality has dropped to 3-4% due to effective treatment.
SARS Statistics: Mortality by Age
01/26/28.01
Mortality was much higher in patients older than 50 years, reaching a mortality rate approaching 50% for this subgroup of patients.
Section 3: 2019-nCoV incidence data
26.01-28.01 TODO: Обновить всю статистику в течении 1-7 дней.
Statistics: mortality probability: by age
27.01-28.01
Coronavirus typical mortality probability statistics (Actual)
the probability for those under the age of 24 is below 1%. At the age of 25-44 years — up to 6%, 44-64 years — up to 15%, from 65 years and older — above 55%.
Coronavirus typical mortality probability statistics (Actual)
Of the total number of patients with Chinese coronavirus, 80% are people over 60 years old.
Statistics: probability of infection: by age
27.01-28.01
Compared to non-smokers, smokers are at a significantly greater risk of complications.
29.01
Statistics on the number of cured: (January 28, 2020)
Up to forty-five patients were cured and were discharged from the hospital (49 today).
25% in China were patients with a severe course of infection (of which 16% were severe, 5% were in critical condition and 4% were dead).
29.01
Infected in 2020 by the ages of 28 and 89. The youngest of the deceased is 48 years old, and the oldest is 89, which generally corresponds to age-related mortality rates for coronaviruses:
Probability statistics for other groups
01/27/28.01
People with weakened immunity and chronic diseases are also at risk.
The first death of a doctor from coronavirus was recorded. The first death was recorded in Beijing. A 50-year-old man was injured. On January 8, he visited Wuhan and contracted pneumonia seven days after returning to Beijing.
A 2014 study showed that pregnant women infected with MERS had stillbirths, so similar cases are possible with 2019-nCoV.
Recently, the first case of infection of a child.
There have been cases of infection from asymptomatic carriers.
1
Two people contacted an asymptomatic Chinese woman sent to Germany, (Note. Later, she said that there were symptoms, but not so much)
In all 4 infected, the disease occurred in a mild form. The probability of infection from asymptomatic carriers is rather small.
Statistics: Cure Probability
27.01-28.01
Statistics on the number of cured: (January 28, 2020)
Up to forty-five patients were cured and were discharged from the hospital (49 today).
Statistics: death toll (More data in the chart table. From 11.02)
Каждый день
Statistics: the number of issued
22.02
Healed 21,318
Out: (Healed + Died) -5 (Cases of reinfection): 23765.
23.02
Healed 23,092
Statistics: Number of suspicions
23.02
China:4148(+882)
Statistics: number of common cases
21.02
42,756 (79%) patients with ordinary cases
Statistics: number of severe cases
21.02
11,551 (21%) patients with serious and critical cases.
23 deaths in countries other than China.
24.02
A minimum of 27 deaths.
26.02
A minimum of 50 deaths.
27.02
South Korea 13,11,8
Diamond Princess 4,4,4
Italy 12,11,7
Japan 3,1,1
Iran 19,16,14
Hong Kong 2,2,2
Taiwan 1,1,1
France 2,1,1
Philippines 1,1,1
A minimum of 57 deaths.
Statistics: Cumulative cases (More data in the chart table. From 11.02)
Everyday
Statistics: Cumulative cases (More data in the chart table. From 11.02)
Section 3: Statistics: Country Data
Every day, Spoiler with detailed country information has been deleted so far. Information is outdated
Statistics for the Chinese provinces here: I have more accurate country data.

Another 25 widget cards on which you can monitor the distribution, but I do not have time
Widget for showing the number of cases: (Actual)
- There was information canceled
- Indonesia 8 cases (3 earlier)
- Saudi Arabia 1 case (28th)
- Pakistan 1 case (30th)
- Kenya1 case (28th)
- Equatorial Guinea 1 case (30th)
- Sudan: 2 cases (29th 1 )
- Brazil 9 cases (1 new, 28) 1
Incomplete data from 12/31 to 02/19
Incomplete data for the entire period
More details also:
1
Recent WHO report synced plus data from other sources
 Photo widget to calculate the number of infected
Photo widget to calculate the number of infected
Section 3: Statistics: Notes and Summary
10.02 Some of the data on the schedule disappeared, I had to reload.
Good news. Judging by official data, distribution is slowing down. Because of this, the boundaries of the forecast are quite large.
Perhaps the lag from antiviral measures already affects. The speed of distribution according to official sources has decreased. Good news.
My statistics, some of the data may differ
14.02
Such a large replenishment of the 13th number is associated with a possible peak. However, due to the refusal in China to take statistics of patients without symptoms, the statistics are distorted. Is peak falsification possible?
Statistics: Summary
26.01-28.01
It’s already possible to admit much higher base mortality (not considering the factor of good treatment),
perhaps the healthcare system is at the limit of its capabilities. In the worst case, the ratio of mortality to infected can increase to SARS with the increasing collapse of the healthcare system.
We can conclude that while the health care system has not reached its limit. Therefore, mortality is still much lower than mortality under normal conditions, without medical care (Basic mortality).
26.01
Unfortunately, it is not known how many actually died, but so far the mortality is lower than that of SARS, and the authorities reacted late to the coronavirus.
That is, mutations may have a negative effect on mortality, but the delayed virus factor cannot be ruled out,
either very lucky / the work of the authorities was more effective compared to 2003. However, there remains a high probability of an increase in the number of cases.
Section 3: Approximate Simple Assessment Scheme
26.01 This section gives the probabilities of a possible development of the situation.
We set the maximum probability for the airport in Wuhan, put a much lower probability for the airports. For airports in other areas and slower transportation methods, while taking the weighted average probability for coronaviruses… for the last 5-7 days before the airport closes
We take a slightly greater probability than from the beginning of the spread, we try to take into account how much could get sick, taking into account the age and probability of catching the disease, as well as the possible consequences of the incubation period, and carry out the calculation.
Statistics: Forecast: Assumptions:
26.01-28.01 TODO: Обновить модель в течении 1-7 дней.
In addition, another assumption is possible: if the number of cases can be greater, then is it possible to increase the number of possible deaths on the basis of these thoughts about the possible number.
In addition: achieving a certain threshold of patients complicates treatment, worsens quality, including through a total shortage of medical supplies.
Therefore, this factor should be taken into account.
And, given the large incubation period, a large number of countries with disease situations, etc.
the number of cases may be greater based on the methods of probabilistic spread of the virus, for example, given the number of passengers transported per day,
for example, only one Wuhan International Airport served 19 million passengers, of which 3,400 flew daily to other countries.
The characteristics of the coronavirus, including especially important: Distribution without symptoms (copy)
01/29?
As the preprint of the medrXiv article emphasizes, carriers spread the virus without any symptoms, which was one of my warnings when I started writing this article a few days ago.
It all depends on what progression the virus will develop before the end of the period.
16.02,? TODO: indicate the news
This has recently been refuted. Symptoms do exist but are very weak. So the danger is partially preserved.
The asymptomatic transmission of the virus has been refuted. Symptoms: muscle pain, fatigue and temperature. The transmission during the incubation period has not been refuted.
1
The characteristics of the coronavirus, including especially important: Distribution without symptoms (copy)
29.01?
The most dangerous indicator is the factor of reproduction of the infection, indicating how many healthy people are infected by one sick person.
This number lies in the range from 3.6 to 4 (approx. 2.0-4.0). And this means that it is necessary to reduce the ways for transmission of the infection in 75% of cases in order to stop the growth of the epidemic. Calculations in the model were carried out according to data on January 21.
According to epidemiologists from the University of Lancaster, the Glasgow Virus Research Center, and the University of Florida Gainesville, only 5% of cases were detected in Wuhan.
For comparison: in the SARS virus in 2003, the infection reproduction factor was 2.0–3.5. However, this virus was not transmitted during the incubation period,
and the symptoms were more pronounced. The reproduction factor after quarantine decreased to 0.4.
The characteristics of the coronavirus, including especially important: Distribution without symptoms Opinion(Копия)
29.01?
Harvard epidemiologist Eric Feigl-Dean emphasizes on Twitter that “he’s never seen a 3.8 *** in his life” and expects a “thermonuclear pandemic.” (*** Most likely for typical coronaviruses)
He also quotes from another study, where the infection reproduction factor is estimated at 2.8.
Summary: Assessment Models for Other Professionals
Statistics: Forecast: Forecast model, 1
26.01-28.01
Perhaps Professor Neil Ferguson of the Center for Global Analysis of Infectious Diseases MRC at Imperial College London, has his own methodology and it is different, they counted at least 1,700 cases yesterday. New data on patients (2000 people) correlate with assumptions. Thus, it is possible today at least 2500-3000 patients hypothetically.
Statistics: Forecast: Forecast model, 2
27.01
Similar calculations are provided by another model presented by experts from Hong Kong. According to SCMP, there are already 44,000 infected in Wuhan, and the infection has spread to all the big cities of mainland China. In this model, the number of cases doubles every 6.2 days.
Statistics: Forecast: Forecast model, 3
27.01
For Wuhan, the 11 millionth city in China that became the epicenter of the epidemic, a team led by Jonathan Reed calculated
that while maintaining the current reproductive factor, there will be 191,529 infected.
Closing cities will not help stop the Chinese coronavirus, although it will delay its spread to some extent, experts say, interviewed by Business Insider.
I also pointed it out above. This will only affect the future situation and that is not so good.
The only plus is low mortality. The only plus is low mortality relative to SARS.
Statistics: Forecast: Forecast model, 4
27.01
According to German experts from the University of Gottingen, there has not yet been a peak in the distribution of 2019-nCoV, and March will be a real test for the world. In this case, the number of infected can exceed the result of SARS (about 8 thousand),
however, I expect a much lower mortality rate than SARS per 1000 cases, not more than 40 people per thousand.
Statistics: Forecast: My model
26.01-28.01TODO: добавить модель
My model is much more modest: See in the «Data on incidence» section, a line for a hypothetical number of cases.
in the future, from 8000 (Confirm already tomorrow or the day after tomorrow) –100,000 people will fall ill until the peak of the incidence rate if the health and quarantine system continues to function,
serious measures will be taken, there will be no serious increase in the number of cases in other countries.
This is the most minimalist statistical forecasting model that I saw (I do not have time, maybe something new has appeared)
16.01
It turned out there was a model similar to me. The minimum indicators of my and other models have already been overcome (SARS). If the epidemic fails, 100 thousand should be within 1-2 weeks.
Statistics: Problems with the study:
04.02
Due to the fact that the study of the most dangerous coronaviruses requires specially trained personnel working in laboratory conditions of biosafety level 3 (BSL-3) or 4,
there are big problems in the study of this virus, and only limited data are available on the survival of the coronavirus and the response to stressful environmental factors.
Regular snapshots of the COVID-19 virus (formerly 2019-nCoV) published at the Rocky Mountains lab at the US National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases in Hamilton, Montana, are published.
Images taken from an electron microscope.
1
The department conducts research on dangerous pathogens like pathogens of Ebola, tularemia, Q fever and others. Biosafety level — IV category (maximum).
In the USA there are about 15 facilities where there is such a level of biosafety.
World Health Organization Advisor Ira Longini has created another model.
according to the model, each infected person under normal conditions infects another 2 or 3 people.
Even if we halve the rate, a third of the world's inhabitants will be infected with the virus, Longini said.
who also heads the Center for Infectious Disease Statistics at the University of Florida.
1
My opinion: I can say that uniformity of infection is almost impossible. There are situations with a positive opportunity for the virus to spread, and vice versa.
«Positive» situations are much less than negative. Therefore, all these models can do little.
Statistics: Forecasting Controversy
16.02: Section moved: follow the link
Analysis of Probable Influencing Factors: Getting Started
Summary:State Response Stages and Forecasts
26.01-28.01
Unfortunately, too much time was allowed between government decisions, as is usually the case.
However, in other countries, a partially authoritarian model would probably be worse; everyone will only know when it reaches a certain stage of danger.
26.01-28.01
After the threat was acknowledged, the government’s overall response level was quite high, however, it was expected that there would still be punctures for people, for example, the same video of dead people lying with the living.
16.02.Прим
However, they say that these videos are from 2003 (SARS Epidemic). Therefore, the quality of the shooting is not very high.
16.02TODO:
In democratic models, timely response to a situation is called into question.
The slow response of the authorities of any country is almost an axiom.
Closing millions of cities a couple of days after the discovery of the disease is fantastic.
According to the correlative model (danger — what needs to be done) of a state’s response, this will only happen if the danger is recognized.
In other cases, the response will be at least a week later with significant danger.
Nobody will lose money at city closures to a certain level of danger. This is the main truth about the relative model of response.
Thus, the reaction time of the authorities and the closure of cities with a million people can be called very good. Nobody has yet covered the cities of millionaires.
If 8 doctors together Li Wenliang achieved success, we could talk about an almost perfect response.
In the image below, I present the differences between response protocols and hazards including lag due to the incubation period.
The difference between a real response protocol (commensurate with the situation) and a hard response protocol.
 Map of the spread of a typical virus
Map of the spread of a typical virus
Protection Features: Treatment Methods (Copy))
27.01-01.02TODO: Добавить методы лечения
There are methods that can alleviate the most dangerous symptoms of the virus:
It is now known that as a temporary measure to reduce the symptoms of coronavirus, Chinese patients are treated with two HIV drugs — a combination of lopinavir and ritonavir, writes Bloomberg. No effective antiviral drugs against the virus exist today.
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (EXMO) — oxygen saturation of the blood makes it possible to survive the most dangerous symptoms.
01/22/01/02
The use of various types of inhibitors.
For example, Favipiravir is a synthetic antiviral drug that was developed back in 1998 in Japan (Toyama Chemical / Fuji Film). The drug is active against RNA viruses and was used in Japan in 2014 to stop the flu epidemic.
So the drug is not new at all and will not be a salvation for everyone. At best, there will be a weakening of symptoms for those already infected. So there’s no point in buying such drugs healthy.
According to Reuters, chloroquin phosphate, which is intended for use against malaria, has also been shown to be effective in inhibiting a new coronavirus infection.
That is, the drug is intended to suppress the performance of the virus. Such drugs are not a panacea. Such (mainly inhibitors) drugs are at least 50-100 pieces.
2019-nCoV; RdRp influenza Favipiravir Inhibits RdRp • Approved for influenza in Japan • Randomized trial for 2019-nCoV (ChiCTR2000029544, ChiCTR2000029600)
2019-nCoV, MERS, SARS, RSV, HCV RdRp Ribavirin Inhibits the synthesis of viral RNAi mRNA • Approved for HCV and RSV • Randomized trial for 2019 nCoV in (ChiCTR2000029387). • Randomized ARVI test
2019-nCoV RdRp Penciclovir Inhibits RdRp Approved for HSV
2019-nCoV, MERS, SARS RdRp Remdesivir (GS-5734) • Stage 3 for 2019 nKoV (NCT04252664, NCT04257656) • Stage 1 for Ebola (NCT03719586)
and 65 more… Read more:
www.nature.com/magazine-assets/d41573-020-00016-0/17663286
Protection Features: Vaccines (Copy)
27.01-01.02
Now scientists are testing, including previously manufactured vaccines, for other coronaviruses at 2019-nCoV, as just announced
Xu Wenbo, head of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Another scientist is trying to enter the country and test samples. Success can make a difference. Otherwise, it will take a very long time to wait for the vaccine, up to several years.
The US and Russia are already developing the first vaccine options. A certain result is possible in a few months. Research and development are ongoing for MERS-CoV.
Summary: Hazard Assessment
Unfortunately, due to the large incubation period and possible mutations, various changes are still possible, the relatively small number of deaths can be misleading.
Many hint at low mortality compared to conventional SARS, but not only mortality can make it dangerous, but also the high possibility of mutations, a large incubation period, high infectivity and possible cross-species infection of creatures, the possibility of «silent» spread, and other factors that may change the overall situation.
Summary: Possible origin: Virus transmission routes: (Copy)
04.02
here is information about the high infectivity of the virus during the incubation period. This was stated at a press conference in Beijing by the Head of the State Committee for Healthcare of the People's Republic of China, Ma Jiaovei.
Some experts do not believe about the contagiousness of the virus during the incubation period.
“I seriously doubt that Chinese government officials have any evidence to support this claim. I don’t know any evidence that over 17 years of work with SARS and MERS coronaviruses (they often compare the new coronavirus 2019-nCoV with them — ed.), It was discovered that someone got infected during the incubation period, ”said Michael Osterholm, Director of the Center for Research and Policy on Infectious Diseases at the University of Minnesota.
Summary: Possible origin: Interspecific distribution
26.01-28.01
With a high probability, the new virus is not so scary compared to SARS (due to greater mortality) and especially hCoV-EMC (due to cross-species reproduction of the virus).
I consider the latter to be the most dangerous, due to the unspecified type of receptors through which the virus is transmitted, which may be an omen of the emergence of a new cross-type virus,
transmitted from animals to humans, and humans to animals without restriction.
Summary: Hazard assessment: Interspecific distribution
26.01-28.01
The mortality rate of this 2019-nCoV is not so high, and only certain age groups have a high probability of dying.
16.02
However, there is a chance that even relatively young people will die, for example, the death of Li Wenliang.
Summary: Hazard Assessment: Health System Limits
26.01-28.01
However, the health care system has its limits. With a significant increase in the number of infected, there will be a large deterioration in the quality of treatment. And it is confirmed. International assistance is needed in this matter.
According to press reports, now in Wuhan, there are not enough doctors or tests for the virus. Patients spend hours in queues waiting for admission, and rapid tests are carried out only for those who have the most pronounced symptoms: temperature, cough, shortness of breath.
Summary:Risk assessment: The duration and the «tails»
26.01-28.01
Unfortunately, the average duration of the disease and its severity is quite high. So it is still not over soon.
Summary: Hazard Assessment: New Year Factor
26.01-28.01
It turns out that the factor of the new year can even help: the population has enough money in their hands to pay for food…
for several months without going to work.
Of course, some people have moved, but earlier.
Summary: Hazard Assessment: New Year Factor, 2 (Copy
26.01-28.01
In addition, about five million residents left Wuhan before the city was closed due to the epidemic of the new coronavirus, the South China Morning Post reports, which is quite possible given the time lag.
Thus, it was not possible to stop the spread of the virus using the usual virus response protocol. Only responding to more stringent protocols is unlikely due to unwillingness to spread panic, substitute power, be deceived if the result is not confirmed, etc.
The factor of the new year, in addition to increasing travel, also has a good side: Many people have enough money to live for several months.
Summary: Hazard Assessment: New Year Factor, 3 (Copy)
26.01-28.01
Summary: Predictive Models
26.01-28.01
Above are various predictive models and their numbers.
Vaccine Development Probability
26.01-28.01TODO: Добавитть из списка новостей
If a positive result is achieved: success in testing earlier vaccines,
everything can be accelerated if the authorities allow them to be used without very long testing.
Vaccine Development Probability 1
26.01-28.01TODO: Добавитть из списка новостей
Regarding the hype: People stock up on masks. Even a medical article talks about this problem with a possible shortage of masks for doctors,
in the US, doctors have contacted suppliers and are monitoring the situation. Reserves of masks may not be long enough.
However, the release of masks is very large. In the end, the situation should bounce back.
Summary:Hazard assessment: The impact of the lag on statistics. Effect of incubation period:
16.02 TODO: Создать статью
Указать на неоднородность передачи вируса. От 2 до 14 дней.
Указать на схожесть графика передачи вируса на древоподобное представление либо паутину.
Указать на «хвосты» начиная от лага заражения и заканчивая лагом выписки или смерти через много дней после. Все это будеи еще долго растягивать продолжительность вспышки.
Указать на минималный строк вспышки с учетом «хвостов» даже если никто уже не заболеет будет еще не менее несколько недель до несколько месяцев.
Summary: The effect of the incubation period
26.01-28.01
Unfortunately, the virus has a large incubation period, which means that the current disease and mortality rates reflect only the number of diseases at the beginning. That is, we now observe only the first group of patients, which appeared at the beginning. Thus, it makes no sense to blame the authorities for the impossibility of stopping the disease. The influence of the current restrictions made by the government will be, for example, to reduce the growth of the exponential growth of the virus in a few weeks or at best to reduce the growth of the infected!
Therefore, the statement by epidemiologists that the results will be visible only after weeks or months is correct.
Outcomes: Impact of the incubation period: Assumption of going beyond the SARS level
26.01-28.01
In addition, the current number of people infected with the first stage may indicate a possible excess of 2003 indicators.
I hope that the curve of increasing the spread of the virus to the peak of the spread of the infection will be o (n) or no more than (n log n).
16.02
So it happened. The number of cases has long gone beyond SARS.
Summary: The effect of the window until the authorities reac
26.01-28.01TODO
The disease had a large gap, where there were no restrictions. Now we are witnessing a situation of an increase in the number of cases during that period.
We will see the impact of measures taken by the government later. The same is with preparation and the usual response to the disease. As a result, being late in any case will be sufficient for the spread of the disease.
Summary: Hazard Assessment: New Year Factor, 2 (Copy)
26.01-28.01
In addition, about five million residents left Wuhan before the city was closed due to the epidemic of the new coronavirus, the South China Morning Post reports, which is quite possible given the time lag.
Thus, it was not possible to stop the spread of the virus using the usual virus response protocol. Only responding to more stringent protocols is unlikely due to unwillingness to spread panic, substitute power, be deceived if the result is not confirmed, etc.
The factor of the new year, in addition to increasing travel, also has a good side: Many people have enough money to live for several months.
The answer to why the authorities' reaction cannot completely extinguish the virus in the chapter: Summary: State response steps and forecasts
Typical misconceptions regarding the virus:
26.01-28.01
Many fakes appear on social networks regarding the virus, supposedly the virus spreads only among the Chinese. However, the first cases of infection of foreigners have already occurred, the first cases of transfer from a foreigner to a foreigner have occurred.
There are also many fakes that are too dramatic. Pointing to hundreds of thousands of infected, or even dead. Despite the relatively long period between the reaction of the authorities, at current rates it is quite difficult to achieve such impressive results.
Some people do not believe in the reality and danger of the virus, compares it with the flu.
The virus is dangerous due to the complex parameters that make this coronavirus dangerous. Starting from possible high infectiousness and ending with severe symptoms.
Some people really more easily pass the symptoms, there may be certain individual characteristics. Some people may actually get slightly infected. Not everyone may have complications in the form of pneumonia. Statistics on the likelihood of illness and mortality hint at this. Some healthy people have a chance to get sick without complications, but it’s better not to risk it. Unfortunately, there are still many blank spots in the study of the virus. However, this does not mean that the virus is a fiction.
Summary: Consequences
26.01-28.01
Highest probability: Substantial material cost to the country. The probability is very high. Danger: Significant damage to the country.
High probability: A new economic crisis. Financial markets are already reacting.
If the interspecific transmission of the virus is confirmed (which I want to ask for verification), the consequences may be worse. Danger: Increase. The probability is average.
If the virus mutates, the consequences can be very different until the effects increase significantly.
If the virus spreads to nearby India, the situation can become very difficult. .Danger: High. Probability: Average, only more than 30 thousand Indian students in the country…
The worst result could be panic. If the authorities cannot control the situation, or scare the population too much. Danger: Colossal. Probability: Very low.
With such a probability, if the population of a billionth country tries to break through the borders, then there will be favorable conditions for the spread of the virus.
A huge chance to infect Indian citizens, which can create the most dangerous migration in the world and part of the population will be sick.
Results: Various negative consequences are possible, up to a very dangerous migration of the infected population, the government may not hold back such massive cases…
I note the chance of individual survival for the population who tried to escape falls even lower than to remain in the current situation.
Unfortunately, it turned out that even technically advanced and powerful countries find it difficult to cope with the consequences alone, so I wanted other countries and organizations to more actively help in this and other cases in order to reduce the likelihood of panic and the worst-case scenario.
Summary: Forecasts and Reality
11.02-13.01
Chinese coronavirus: Hong Kong health experts have called for the adoption of «draconian» measures in the city, since researchers estimate that in Wuhan for 44 000 cases.
In the end, we can say that the minimum prognosis is no longer realistic. (More than 75,000 patients. 35,000 were predicted)
If there were no new cases, my prediction of up to one hundred thousand people would be real.
Due to new cases in the world, it is now likely to infect at least 100,000 people and up to 29,000 thousand.
Summary:Nesseary actions
01/26/28.01
The good news: The WHO IHR Emergency Committee will resume work on a new coronavirus in China to decide if the epidemic is a global emergency.
WHO declared the outbreak of coronavirus a global health emergency. The decision overturned the organization’s decision to postpone the declaration just a week ago.
The declaration does not have the force of law, but is a landmark example for everyone. The declaration of emergencies also adds urgency to any WHO appeal for money.
01/30/20120
The rapid spread of coronavirus caused massive cases of anti-Chinese sentiment. In Japan, the hashtag # ChineseD'tComeToJapan is popular on Twitter.
“Some of the xenophobia is probably due to wider political and economic tensions and concerns about China,
that interact with more recent fears of infection, ”said Christie Gowella, associate professor of Asian Studies at the University of Hawaii, Manoa.
There is a lot of information about the growing domestic contradictions, which is very dangerous.
Now we need to deal with panic. The situation with the loss of control by the authorities is the worst that can be.
Officials say that central China is dangerously short of medicines, despite the fact that the equipment is delivered in bulk from around the world.
The situation is testing the health system for durability. The photographs posted on the Internet show that hospital workers, many of whom are still in protective gear,
exhausted, they fell to their tables and to the floor.
Two of the Japanese citizens who were evacuated from Wuhan refused to get tested for coronavirus, Japanese social media users said
that travelers arriving in Tokyo on Wednesday put the country at risk.
01/26/28.01
Need material support from countries. You need to check the virus as well as hCoV-EMC, an interspecific check of virus transmission, which can provide additional information.
However, this scenario can be avoided by creating worldwide support for those infected, for example, in social networks, including from the states.
In this case, it is quite possible to defeat this outbreak of coronavirus.
Despite these reports, there are several important signs, most likely not taken into account, that could shed light on the characteristics of the virus.
For example: research is needed on the probability of virus survival in an environment outside the body, as well as studies on interspecific transmission of the virus as was done with hCoV-EMC.For example, research is needed on the probability of virus survival in an environment outside the body, as well as studies on the interspecific transmission of the virus as was done with hCoV-EMC.
Analysis of Probable Influences: The Beginning
Initial phase: Response: Medics reaction
In January 2020, a consortium of Chinese medical specialists was tasked with investigating the occurrence of the so-called Wuhan coronavirus or Wuhan pneumonia.
On January 24, 2020, the report was published in The Lancet. The investigation was marked off. The first patient, who was subsequently diagnosed with coronavirus, developed symptoms on December 12, 2019.
A previous case of a patient was discovered who had symptoms since December 1, 2019, indicating an even earlier origin of coronavirus.
Analysis of Probable Influencing Factors: Initial Phase
Initial phase: Response: Medics reaction, 2
The number was already infected on the 30th. Dr. Wenliang, an ophthalmologist from Wuhan, tried to warn Wechat in his account.
One day before the official reaction, a group of doctors could warn of an outbreak. Thus the influence of «whistleblowers».
At the same time, authorities did not allow widespread dissemination of information in China until January 3
1
Then, Li Wenlyan’s information said that a group of seven patients was unsuccessfully treated for symptoms of pneumonia, the virus did not respond to traditional treatment.
Later that day, the medical department of the Wuhan Municipal Health Committee issued an «emergency statement for the treatment of pneumonia of unknown origin»
Initial phase: Response: Reaction of authorities and organizations
December 31, such a report was created, then it was supplemented:
1
December 31, 2019, Wuhan Municipal Health Commission, Hubei Province, China, reported
a group of cases of pneumonia of unknown etiology, with a commonly reported link to the Wuhan seafood market.
In some cases, visits to another food market were reported, while others did not report any relationship with the markets,
but have been in contact with people with respiratory symptoms.
On December 31, 27 cases were reported, thus. Most likely, the basis for distribution was already formed then. Thus, we practically missed the initial stage of infection.
I did not find information in public sources.
On December 31, Hong Kong, Macau, and Taiwan immediately stepped up arrival control processes.
1st numbers the fish market has already closed.
Initial phase: Response: Media respons
The first chronology was created on the Worcestershake of Vorutgale already on the 31st! <a href=«
pt.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cronologia_do_surto_do_novo_coronavírus_2019-nCoV> 1
Many thanks to them, thanks to them I got more information for analysis.
Analysis of Probable Influencing Factors: Initial Phase: Assumptions
Initial phase: Probability: Assumption: The probability of an outbreak starting earlier
Given the onset of symptoms in probably one of the first patients on December 1, 2019, and given the probable term for the development of symptoms.
Possible influence of factors:
Initial phase: Probability: Proposition No. 1: Total
We have a significant chance of a start. The „window of opportunity“ for the spread of the virus can be much larger.
Due to the large lag of the incubation period, the number of patients in the first period most likely affected the second.
However, the size of the „window“ still surprises me.
Initial phase: Probability: Proposition No. 1: The main factors influencing statistics
At the first stage, many parameters have a greater level of criticality.
The course of the development of the disease in the initial stages can significantly change
Internal Factors: Reaction Probability Factors
Internal Factors: Symptoms
Internal factors of the statistical system
Internal factors associated with common indicators
External factors associated with common indicators
Internal factors associated with the virus disseminators
External factors associated with the virus disseminators
Internal factors associated with the control system
Summary: Key factors
21.02
First primary factor: Severity
The first major factor can be considered the severity of the disease. On the one hand, an ideal virus should cause greater severity, but over time, allowing the virus to spread while patients are still alive and can move around.
Thus, severity affects patient mobility. It will be difficult for a patient in serious condition to infect many. The most negative scenario for the virus. The severity is too high, all patients died without being able to infect anyone.
More positive for the virus is low severity but high infectivity. However, in this case, he should not threaten peace.
Thus, an “ideal virus” needs to be “delayed increase in severity”. In this case, you can infect a lot of people (Mobility will be sufficient), and then they will die.
So our coronavirus is really „very advanced“ in this direction. Very close to the perfect virus. If the severity was a little higher and modern means did not allow saving people, we could talk about incredible danger.
The average number of infected from 1 patient (R0) from 1.2 to 3.0. This can be compared with figures in the initial periods of SARS, H1N1 infections. Usually, R0 decreases with time. It is also affected by the survival of more aggressive forms of the virus and disease control measures. Some viruses can degenerate into less dangerous, but less dangerous can occur regularly.
The same SARS and MERS had higher mortality and did not have the expressed benefits of delayed symptoms. Epidemics quickly came to naught, despite a lower level of technology then.
Second primary factor: Infectiousness (Contagiousness)
21.02
The second main factor is infectiousness (This is a complex parameter): How many people can infect a person, what radius of the patient’s path is dangerous, what number of infection routes. how the protection methods influence infectiousness… Here the ratio is direct. The more infectious the worse for us.
Restrictions on the possibility of infection and the “target group” reduce the chances of the virus. The same SARS and MERS required long-term close contact and genetically determined susceptibility to the pathogen.
However, MERS seemed to circumvent these features and really could be transmitted without ACE2, fortunately lucky. However, MERS oddly enough has an attachment to the place.
Outbreaks are still ongoing (in 2019, 152 cases, 51 people died). Recently, Saudi Arabia seems to have reported a small outbreak, just before 2019nCOV.
In addition, the main focus of the disease has almost exhausted itself. The main factors are likely to be other foci. If there is a new “wide corridor” for distribution, the situation may continue.
In other cases, the epidemic will decline. Thus, other countries are in the focus of attention now.
The increase in the number of diseases in China continued and almost returned to normal +835 infected in China, having read + ~ 500 on the last day.
Disease growth in other countries has begun to affect overall statistics. Already registered 1076 cases of infection.
Given this, the situation will not be changed for a few more weeks.
New disease rates can jump every day, depending on the situation.
So there are 3-4 countries at risk. If everything goes well with them, the epidemic will be over.
The first country is Singapore (A man went to hospitals for a week until he was hospitalized), South Korea (A man went to church, infected parishioners), Japan (They say that quarantine is of insufficient quality), and also Thailand.
If the virus finds sufficient pathways to spread and there will be a fairly vulnerable population (or other criteria, see paragraph: criteria), you can expect a change in the situation.
Third main factor: Delayed action
The third major factor is the effect of the delayed effects of treatment and infection. Here the virus also has advantages. It’s hard to predict such hidden indicators.
Fourth main factor: mutability
The fourth major factor is mutability. Coronaviruses are more prone to this than part of other viruses. We will see.
Fifth major factor: incubation period
The fifth major factor is contagiousness during the incubation period and incomplete manifestation of symptoms, or partial manifestation.
Sixth main factor: Technical level of treatment
21.02
Sixth main factor: Technical level of treatment. We were lucky. If we encountered such a coronavirus in the 1920s, the situation would probably be repeated.
Due to the large number of factors, we cannot get a “clean script”. Many considered this the case on the ship, but this is not so. There the virus had its own characteristics.
They talk about ventilation and a large number of people from vulnerable groups. Thus, this option will not work either.
So it’s only partially possible to try to take a case on a ship as an example. An “ideal” test can only be testing under practically ideal conditions without modern treatment, which is absurd, of course.
We will save people and not try to find out the real mortality and spread of the virus.
Probably in a “perfect test” one could get the result and maybe it would be comparable to Spain.
But don’t worry, while the health care system is working and there are advanced treatments, this should not be repeated.
I hope you now understand how important the healthcare system and research are. Perhaps we have already partially crossed the limit of critical vulnerability to diseases of the level of Spain.
So I hope that in a country with poor quality of health care a similar case does not happen. In other cases, everything should be fine.
Seventh Core Factor: Distribution Capability Level
21.02
Seventh main factor: Level of distribution: This is affected by the means of movement, the number of people, the number of mass events, etc.
One of the most important elements can be typical places with vulnerable groups of the population.
One such place is the hospital and church markets. All places have almost been featured in statistics. For example, 155 people are already sick in Korea. Many patients were parishioners.
in hospitals, firstly, a sufficient number with chronic diseases, including a large number of other vulnerable groups. In churches, there is also a high probability of finding representatives of vulnerable groups.
Markets are a more traditional form of purchase for some population groups, unlike online orders and supermarkets.
In addition, a market like Wuhan served Yeshe and medical destinations. Many items in these markets are for traditional treatment.
Part of the population of China, the new middle class is already eating in restaurants, cafes, etc.
Thus, the market in Wuhan was a very favorable place as a base point for the spread of the virus: A large number of vulnerable populations, including treated with folk remedies.
About a large number of animals in such a market and conditions already mentioned above. Particular care must be taken to protect or suspend some of the vulnerabilities.
Postscript: I only state the facts and condemn any attempts at xenophobia for various reasons. As the head of WHO said: “This is a time for facts, not for fear. This is a time for science, not rumors. This is a time of solidarity, not a witch hunt ...”

The influence of various factors on the statistics.
Isolated cases in the context of general statistics.
Decoding infographic:
If you want to count cases, you need to understand that we are trying to translate three-dimensional multi-threaded cases into statistics.
At the bottom are individual people and their movement graphs. This can be depicted as a tree from 1 person to another. Round indicators: these are the cases that fell into the border of an airborne or other effect. Depending on the form of severity (Until a person usually begins to feel bad), he will move, especially in the initial periods when there is no quarantine.
The different lengths of such contacts (length of the incubation period) and the length of the recovery period also affect the statistics.
Further, cases usually spread in certain places: For example, a ship (highlighted in squares). Each such place has its own characteristics. Part of places with a large concentration of vulnerable populations can lead to a difficult situation. Then territorially go disease zones all the way to countries.
Thus, I have already said that the market was almost an ideal place to start the coronavirus.
As a result, these small cases with each individual infected can greatly affect the statistics. A huge number of factors at the lower and higher levels affect the statistics. The main factors (More than a hundred) and the degree of their influence I have already written in the table above.
Summary: The Need for Global Valuation Systems
21.02
Thus, there are a huge number of factors that have their own characteristics. All this needs to be known in order to predict the spread of the virus. Otherwise, it is a fortune-telling on coffee grounds.
It is very important to create global forecasting systems trusted by many who really collected the big picture from incomplete and partially conflicting information.
19.02
As a result, we have a huge number of factors that need to be considered when calculating indicators. Data on several factors is almost impossible to get.
As a result, I am always skeptical about the calculation
Other links
Human Coronavirus EMC Does Not Require the SARS-Coronavirus Receptor and Maintains Broad Replicative Capability in Mammalian Cell Lines — — mBio, 11.12.2012, doi: 10.1128/mBio.00515-12
Тяжёлый острый респираторный синдром
2019-nCoV
Infectiousness research
Opinion of the epidemiologist
www.medrxiv.org
china-coronavirus-hong- kong-medical-experts-call
Receptor binding domain as a target for the development of SARS vaccines.
WHO case report
WHO website
Essential drugs for treating the virus
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Up
Part of the links
Updated Charts for 2019-nCov
New News: (Changed)
.
Link
RUSSIAN DOCTORS MEMES(TRANSLATED)
Croatia: 3 cases
Pakistan: 2 cases
Estonia 1 case
Georgia 1 case
Greece 1 case
Norway 1 case
Macedonia 1 case
Switzerland 1 case
Denmark 1 case
The first test of a 61-year-old Brazilian for coronavirus was positive.
Despite the coronavirus, the ministers of health of France, Germany, Italy and the European Commission committed themselves to keep the borders open.
A 26-year-old Ukrainian woman, in Cremona, Lombardy, was infected with COVID-19.
In Paris, a Frenchman died. The man was 60 years old, reports BFMTV.
The WHO leader said the sudden increase in coronavirus cases in Italy, Iran and South Korea is “a matter of deep concern,” but the virus is still possible to contain in order to avoid a pandemic.
Intermediate carrier animals of the coronavirus COVID-19 may be domestic, wild, or domesticated wild animals that have not yet been identified by virologists. This was reported by the press service of the Ministry of Health.
Note: I recall a likely intermediate carrier has long been identified. This is a pangolin.
Epidemiologists say the mortality rate is 3.5%, while outside the Chinese province of Hubei, where the epidemic began, 0.79%
Given the long incubation period of COVID-19, during which the carrier is already contagious, the actual number of cases may be about 7 million people.
Moderna, an American biotechnology company, is preparing a vaccine for human clinical trials.
The first vaccine samples were sent to specialists from the US National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID),
The Wall Street Journal reported February 25.
Three Russian citizens evacuated to Kazan with a Diamond Princess confirmed the diagnosis on February 26. That is, Russia already has 5 cases.
In total, there were 24 Russian citizens aboard the ship.
Russia was able to get COVID-19 and has already developed five vaccine prototypes, said Deputy Prime Minister Tatyana Golikova, a RBC correspondent reports.
The XXXII Summer Olympic Games, which are scheduled for the period from July 24 to August 9 in Tokyo, can be postponed for a year, The XXXII Summer Olympic Games, which are scheduled for the period from July 24 to August 9 in Tokyo, can be postponed for a year,
Davis Cup (Tennis) matches in Japan will be held without spectators
Hong Kong launches $ 15.4 billion stimulus program for economy
Each permanent adult in Hong Kong will receive 10,000 local dollars, and business — affordable loans and tax cuts
And the business will receive loans at a low interest rate with a 100% government guarantee in the amount of up to 2 million Hong Kong dollars ($ 260,000). They also promise a 100% reduction in income tax rates to Hong Kong $ 20,000 ($ 2,600) inclusive.
Georgia establishes medical control on the border with Azerbaijan due to coronavirus
Tourists from Russia more often refuse to travel to Italy and Europe.
Asian Champions League football matches postponed in South Korea
In St. Petersburg, the Chinese Culture Festival will take place, but without the Chinese.
South Korea offered to distribute masks for free
1.7 thousand people quarantined in Iraqi Kurdistan
International Exams Postponed in Iran
One of the largest US airlines Hawaiian Airlines will suspend flights to South Korea
On February 26, the foreign ministers of South Korea and China had a telephone conversation during which they discussed the situation with coronavirus.
Saudi Arabia has closed the entrance for pilgrims
On the evening of February 26th, bars in the Italian province of Lombardy (Milan) reopened to visitors.
In Nizhnevartovsk (Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug), neighbors harassed a family from China and forced them to leave the region.
In Russia, authorities gave grocery chains instructions for combating coronavirus
Moscow restaurants ordered to increase dishwashing due to coronavirus
Cruise liner from Italy MSC Meraviglia did not receive permission to call in Jamaica and Georgetown.
26/02Cut)
25.02(Cut)
24.02, 2020(Cut)
23.02, 2020(Cut)
Note As I said earlier, the dynamics in these countries will affect the end of the outbreak of coronavirus worldwide.
So there are already more than six „critical countries“ :( Yesterday it was 3-4). If everything goes well with them, the epidemic will be over.
First country: Singapore (A man went to hospitals for a week until he was hospitalized).
Second country: South Korea (Man went to church, infected parishioners)
Third country: Japan (They say that there is insufficient quarantine)
Fourth country: Iran. Everything happens too fast. Tomorrow there may be at least 25-30 patients!
Fifth country: Thailand.
Sixth country: Italy. 56 cases per day (There were 14).
The number of coronavirus infected in Italy has increased to 79 people.
The virus continues to spread. The new forecast is more than 100,000 worldwide and China. Previously, a forecast of up to 100,000 in China was the most likely among all.
The situation is developing in different countries, so it is even more difficult to predict. Everything may end or the fate of China in 1 of the countries will be repeated.
February 22, 2020(Cut)
I did not understand what happened in Italy. Why so much sick.
Already 18 growth per day. 10 cities have already been isolated in Italy.
First European dies of coronavirus in Italy
I did not understand what happened in Iran. There were only a few patients yesterday, yesterday there were only 6 patients in Iran.
13 new cases of COVID-19 have been reported in Iran, including two deaths.
According to Iranian Ministry of Health spokesman Kianush Jahanpur, most patients with coronavirus were either residents of Qom or recently visited the city.
Thus, to date, 18 cases of the disease have been confirmed in Iran, including four dead.
Most of the patients (more than 700) were identified in Japan, of which more than 600 passengers and Diamond Princess crew members.
The Yonhap news agency reported Saturday morning, 142 new cases were detected in South Korea, with a total of 346 people.
In Singapore, 86 patients, in Hong Kong — 69, Thailand — 35, in Taiwan — 26, in Malaysia — 22, Iran — 18, Australia -17, Germany, Vietnam, and the USA — 16 each, in France — 12, in Macau — 10.
Note As I said earlier, the dynamics in these countries will affect the end of the outbreak of coronavirus worldwide.
So there are already more than six „critical countries“ :( Yesterday it was 3-4). If everything goes well with them, the epidemic will be over.
First country: Singapore (A man went to hospitals for a week until he was hospitalized).
Second country: South Korea (Man went to church, infected parishioners)
Third country: Japan (They say that there is insufficient quarantine)
Fourth country: Iran. Everything happens too fast. Tomorrow there may be at least 25-30 patients!
Fifth country: Thailand.
Sixth country: Italy. 14 cases per day.
If the virus finds sufficient pathways to spread and there will be a fairly vulnerable population (or other criteria, see paragraph: criteria), you can expect a change in the situation.
See an article on factors for more details.
It is already pointless to think that everything will end within 1-2 weeks.
Knocks 504 error (Timeout). I had to cut the news
.
The rest is here 
 Some people had no connection with the market
Some people had no connection with the market
Incomplete data for the entire period

 The influence of various factors on the statistics.
The influence of various factors on the statistics.