Базовые алгоритмы на графах
- воскресенье, 6 августа 2023 г. в 00:00:19
Всем привет! Меня зовут Нурислам (aka tonitaga), и сегодня я бы вам хотел рассказать об Базовых алгоритмах на графах.
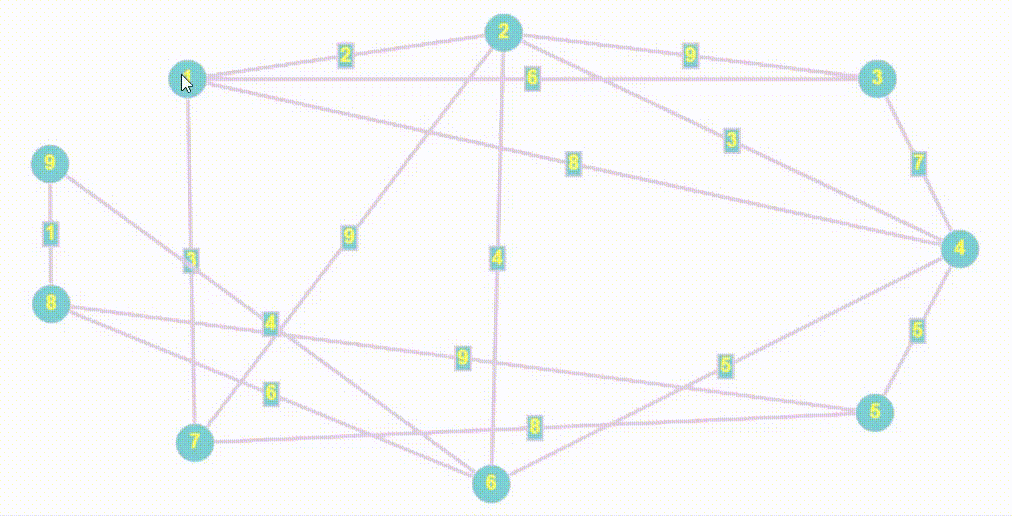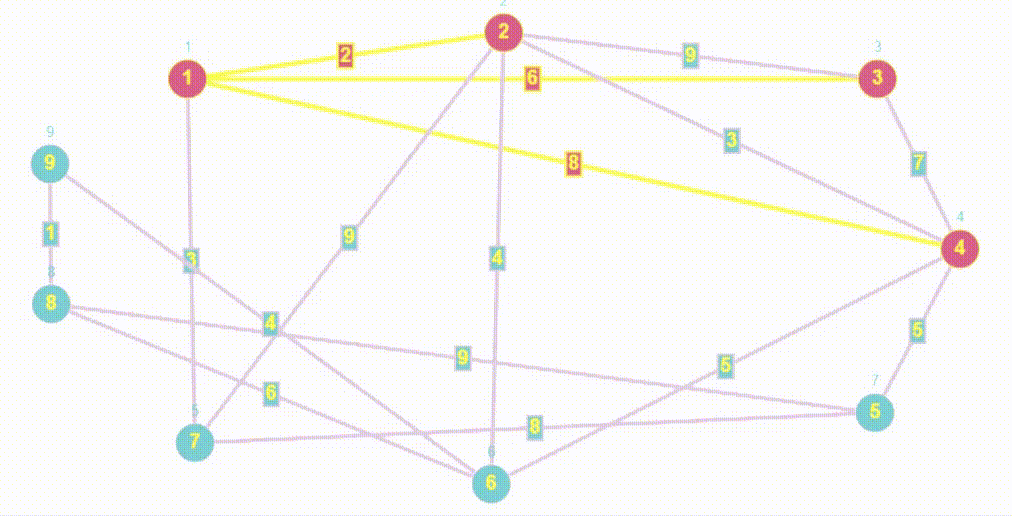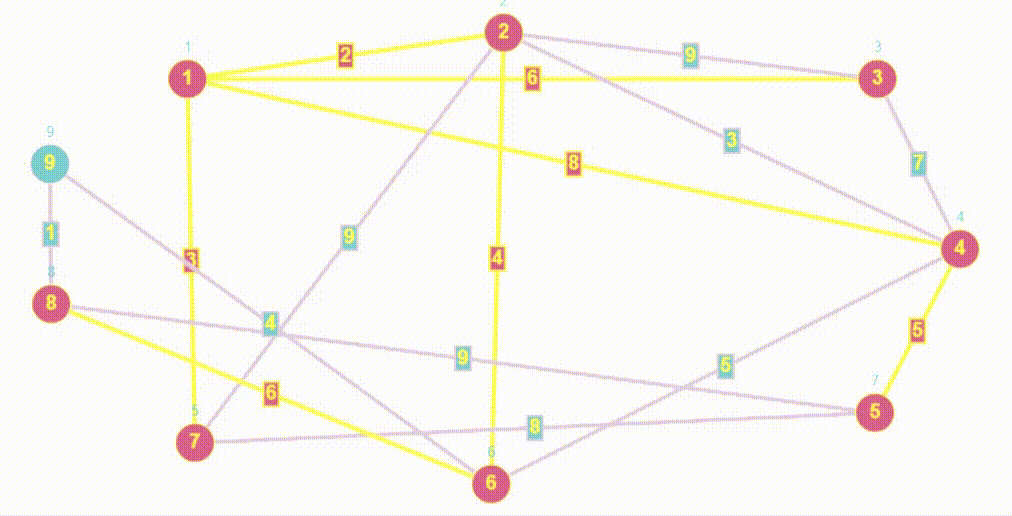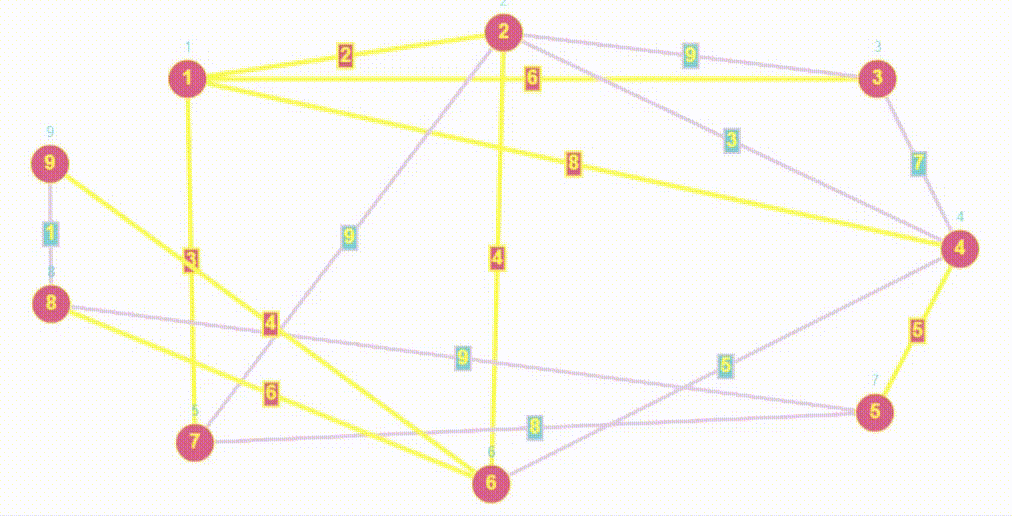

std::vector<int> BreadthFirstSearch(Graph &graph, int start_vertex) {
if (start_vertex > graph.GetVertexesCount() or start_vertex <= 0)
return {};
std::vector<int> enter_order;
std::vector<short> visited(graph.GetVertexesCount());
std::queue<int> q;
// Функция принимает вершину, нумерация которой начинается с 1
// Для удобства уменьшаем ее значение на 1, чтобы нумерация начиналась с 0
--start_vertex;
visited[start_vertex] = true;
q.push(start_vertex);
enter_order.emplace_back(start_vertex + 1);
while (!q.empty()) {
auto from = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int to = 0, size = graph.GetVertexesCount(); to != size; ++to) {
if (!visited[to] and graph(from, to) != 0) {
visited[to] = true;
q.push(to);
enter_order.emplace_back(to + 1);
}
}
}
return enter_order;
}std::vector<int> DepthFirstSearch(Graph &graph, int start_vertex) {
if (start_vertex > graph.GetVertexesCount() or start_vertex <= 0)
return {};
std::vector<int> enter_order;
std::vector<short> visited(graph.GetVertexesCount());
std::stack<int> s;
--start_vertex;
visited[start_vertex] = true;
s.push(start_vertex);
enter_order.emplace_back(start_vertex + 1);
while (!s.empty()) {
auto from = c.top();
bool is_found = false;
for (int to = 0, size = graph.GetVertexesCount(); to != size; ++to) {
if (!visited[to] and graph(from, to) != 0) {
is_found = true;
visited[to] = true;
s.push(to);
enter_order.emplace_back(to + 1);
from = to;
}
}
if (!is_found)
s.pop();
}
return enter_order;
}Заметим, что код практически ничем не отличается, поэтому их можно объединить в одну функцию, и передавать туда просто тип контейнера
//
// If Container type = std::stack<int> it will be DepthFirstSearch
// If Container type = std::queue<int> it will be BreadthFirstSearch
//
template <typename Container = std::stack<int>>
std::vector<int> FirstSearch(Graph &graph, int start_vertex)
{
if (start_vertex > graph.GetVertexesCount() or start_vertex <= 0)
return {};
constexpr bool is_stack = std::is_same_v<Container, std::stack<int>>;
std::vector<int> enter_order;
std::vector<short> visited(graph.GetVertexesCount());
Container c;
--start_vertex;
visited[start_vertex] = true;
c.push(start_vertex);
enter_order.emplace_back(start_vertex + 1);
while (!c.empty()) {
int from = -1;
if constexpr (is_stack) from = c.top();
else {
from = c.front();
c.pop()
}
bool is_found = false;
for (int to = 0, size = graph.GetVertexesCount(); to != size; ++to) {
if (!visited[to] and graph(from, to) != 0) {
is_found = true;
visited[to] = true;
c.push(to);
enter_order.emplace_back(to + 1);
if (is_stack)
from = to;
}
}
if (is_stack and !is_found)
c.pop();
}
return enter_order;
}std::vector<int> BreadthFirstSearch(Graph &graph, int start_vertex) {
return FirstSearch<std::queue<int>>(graph, start_vertex);
}
std::vector<int> DepthFirstSearch(Graph &graph, int start_vertex) {
return FirstSearch<std::stack<int>>(graph, start_vertex);
}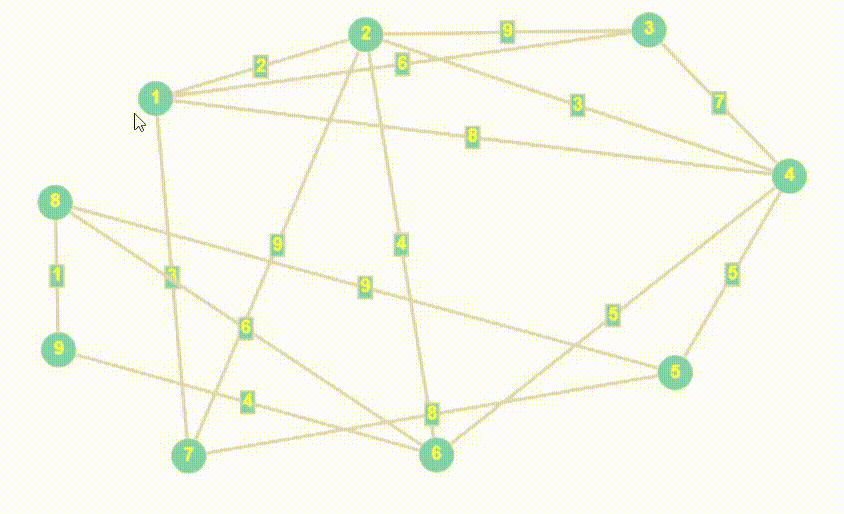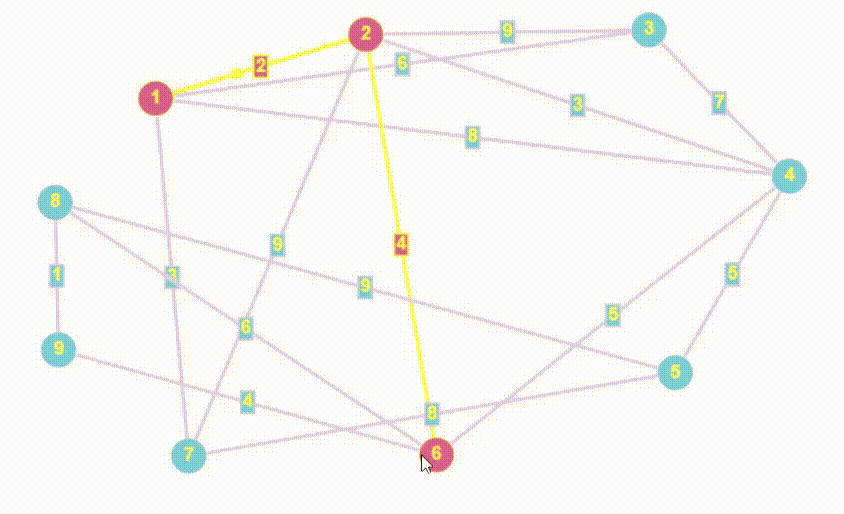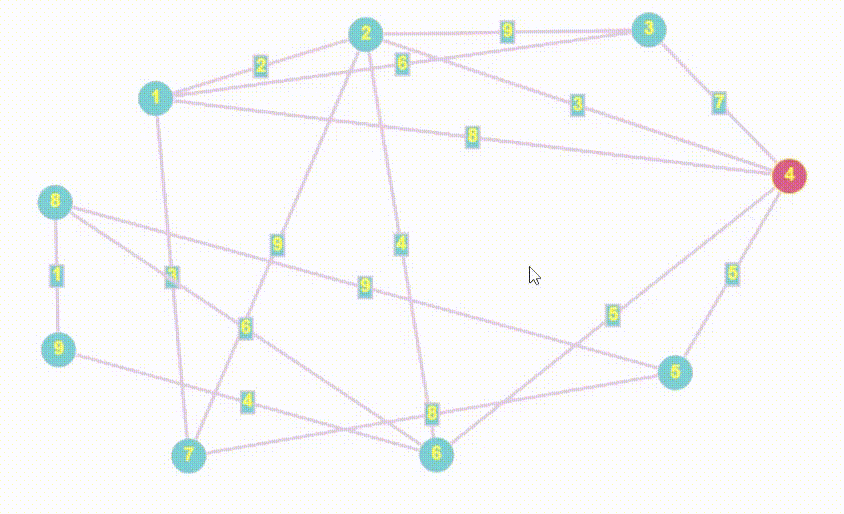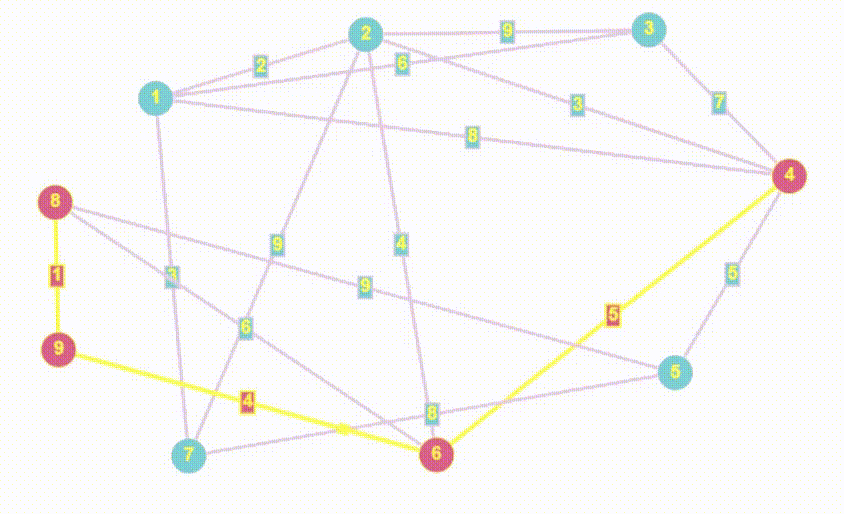
int GetShortestPathBetweenVertices(Graph &graph, int start, int finish) {
if (start <= 0 or finish <= 0 or start > graph.GetVertexesCount() or finish > graph.GetVertexesCount())
return kInf;
std::vector<int> distance(graph.GetVertexesCount(), kInf);
--start, --finish;
distance[start] = 0;
std::set<std::pair<int, int>> q;
q.insert({distance[start], start});
while (!q.empty()) {
auto from = q.begin()->second;
q.erase(q.begin());
for (int to = 0, size = graph.GetVertexesCount(); to != size; ++to) {
bool edge_is_exists = graph(from, to) != 0;
bool new_edge_is_shorter = distance[to] > distance[from] + graph(from, to);
if (edge_is_exists and new_edge_is_shorter) {
q.erase({distance[to], to});
distance[to] = distance[from] + graph(from, to);
q.insert({distance[to], to});
}
}
}
return distance[finish];
}По коду можно увидеть явные признаки схожести с BFS, я даже специально множество назвал как q, потому что в данном случае множество отыгрывает роль псевдо-очереди


Matrix<int> GetShortestPathsBetweenAllVertices(Graph &graph) {
const int vertexes_count = graph.GetVertexesCount();
Matrix<int> distance(vertexes_count, vertexes_count, kInf);
// Пункт 2
for (int row = 0; row != vertexes_count; ++row) {
for (int col = 0; col != vertexes_count; ++col) {
distance(row, col) = graph(row, col) == 0 ? kInf : graph(row, col);
if (row == col)
distance(row, col) = 0;
}
}
// Пункт 3 (Постепенно открываем доступ к новым вершинам)
for (int v = 0; v != vertexes_count; ++v) {
// Пункт 3.1 (Пробегаемся по матрице distance)
for (std::size_t row = 0; row != vertexes_count; ++row) {
for (std::size_t col = 0; col != vertexes_count; ++col) {
int weight = distance(row, v) + distance(v, col);
if (distance(row, v) != kInf and distance(v, col) != kInf and distance(row, col) > weight)
distance(row, col) = weight;
}
}
}
return distance;
}Написать реализацию гораздо проще, чем понять как этот алгоритм работаем, поэтому советую ознакомиться с видео
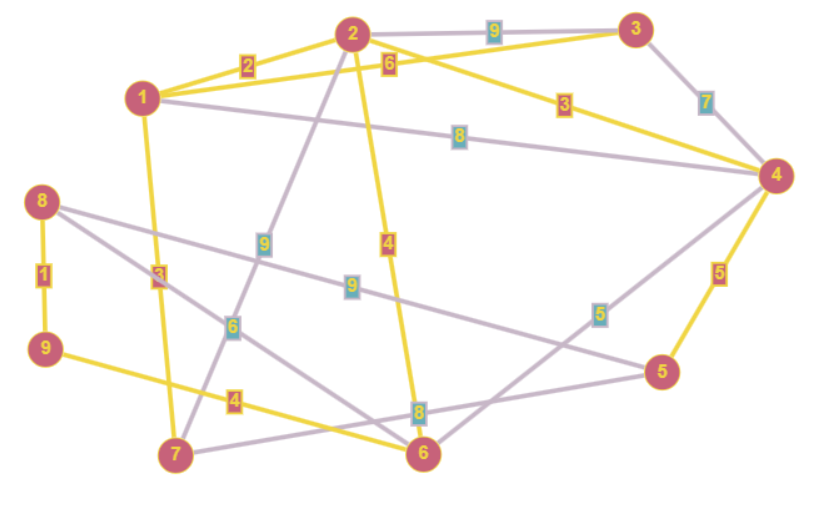
Скажу сразу, что моя реализация не умеет работать с графами у которых, есть изолированные вершины, как только я это сделаю я изменю статью, спасибо за понимание.
Matrix<int> GraphAlgorithms::GetLeastSpanningTree(Graph &graph) {
const auto vertexes_count = graph.GetVertexesCount();
Matrix<int> spanning_tree(vertexes_count, vertexes_count, kInf);
std::set<int> visited, unvisited;
std::vector<Edge> tree_edges;
for (int v = 0; v != vertexes_count; ++v)
unvisited.insert(v);
{
// Вершина должна браться случайно, но какая разница, если дерево статичное.
// Дерево независимо от start_vertex всегда одинаковое
const auto start_vertex = static_cast<int>(vertexes_count / 2);
visited.insert(start_vertex);
unvisited.erase(start_vertex);
}
// Initialize Finish -> Start main loop
while (!unvisited.empty()) {
Edge edge(kInf, kInf, kInf);
for (const auto &from : visited) {
for (int to = 0; to != vertexes_count; ++to) {
bool is_unvisited_vertex = unvisited.find(to) != unvisited.end();
bool edge_is_exists = graph(from, to) != 0 or graph(to, from) != 0;
if (edge_is_exists and is_unvisited_vertex) {
int existed_weight = graph(from, to) == 0 ? graph(to, from) : graph(from, to);
bool edge_is_shorter = edge.weight > existed_weight;
if (edge_is_shorter)
edge = {from, to, existed_weight};
}
}
}
if (edge.weight != kInf) {
tree_edges.emplace_back(edge);
visited.insert(edge.vertex2);
unvisited.erase(edge.vertex2);
} else {
break;
}
}
// Initializing spanning tree
for (const auto &edge : tree_edges) {
spanning_tree(edge.vertex1, edge.vertex2) = edge.weight;
spanning_tree(edge.vertex2, edge.vertex1) = edge.weight;
}
return spanning_tree;
}